Introduction
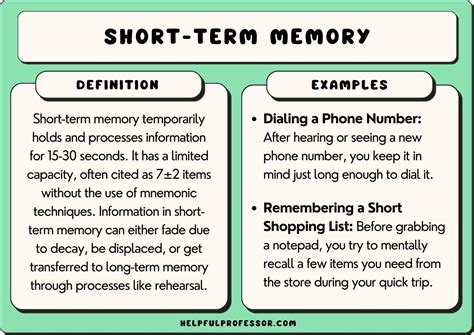
Working memory, also known as short-term memory, is a cognitive system that temporarily stores and manipulates information for use in ongoing cognitive tasks, such as comprehension, learning, and reasoning. Working memory is essential for everyday activities, such as remembering a phone number while dialing, following directions while driving, or solving a math problem in your head.

Capacity and Duration of Working Memory
The capacity of working memory is limited, both in terms of the amount of information that can be stored and the duration for which it can be retained. The average person can hold about seven items in working memory at once, and these items are typically lost from memory within a few seconds if they are not rehearsed or attended to.
Functions of Working Memory
Working memory serves a variety of functions, including:
-
Temporary storage: Working memory temporarily stores information that is needed for ongoing cognitive tasks, such as remembering a phone number while dialing or following directions while driving.
-
Manipulation of information: Working memory allows us to manipulate information in various ways, such as combining it with other information, comparing it to other information, or transforming it into a different format.
-
Control of attention: Working memory helps us to control our attention and focus on the task at hand, by directing our attention to the most relevant information and ignoring irrelevant information.
The Neural Basis of Working Memory
The neural basis of working memory is complex and involves multiple brain regions, including the prefrontal cortex, the parietal cortex, and the hippocampus. These regions work together to encode, store, and manipulate information in memory.
Applications of Working Memory
Working memory is essential for a variety of everyday activities, including:
-
Comprehension: Working memory helps us to understand language by temporarily storing the words and sentences we hear or read, so that we can make sense of them.
-
Learning: Working memory is essential for learning new information, by temporarily storing the new information so that we can associate it with our existing knowledge.
-
Reasoning: Working memory helps us to reason and solve problems by temporarily storing the premises and conclusions of our arguments, so that we can evaluate them and draw inferences.
Pain Points
-
Forgetting: One of the biggest pain points associated with working memory is forgetting. We often forget things that we need to remember, such as phone numbers, appointments, and names. This can be frustrating and can lead to problems in our personal and professional lives.
-
Distraction: Another pain point associated with working memory is distraction. We are easily distracted by our surroundings, which can make it difficult to focus on the task at hand and to remember the information that we need to remember.
Motivations
-
Improved memory: We all want to have a better memory, and working memory is a key component of overall memory function. By improving our working memory, we can improve our ability to remember things, learn new information, and solve problems.
-
Increased productivity: Working memory is essential for a variety of everyday activities, including comprehension, learning, and reasoning. By improving our working memory, we can be more productive in our personal and professional lives.
-
Reduced stress: Forgetting and distraction can be very stressful. By improving our working memory, we can reduce stress and improve our overall well-being.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Not rehearsing information: One of the biggest mistakes that you can make is to not rehearse the information that you are trying to remember. Rehearsal helps to strengthen the memory trace and make it more resistant to forgetting.
-
Being distracted: Another mistake that you can make is to be distracted while you are trying to remember something. Distraction can interfere with the encoding and storage of information in memory.
-
Trying to remember too much information at once: Another mistake that you can make is to try to remember too much information at once. Working memory has a limited capacity, so it is important to focus on remembering the most important information.
Why Working Memory Matters
Working memory is essential for a variety of everyday activities, including comprehension, learning, and reasoning. It is also important for our overall success in life. By understanding how working memory works, we can take steps to improve our memory and to use it more effectively.
Benefits of Working Memory
There are many benefits to improving your working memory, including:
-
Improved memory: Working memory is a key component of overall memory function, so improving your working memory can improve your ability to remember things, learn new information, and solve problems.
-
Increased productivity: Working memory is essential for a variety of everyday activities, including comprehension, learning, and reasoning. By improving your working memory, you can be more productive in your personal and professional life.
-
Reduced stress: Forgetting and distraction can be very stressful, so improving your working memory can reduce stress and improve your overall well-being.
-
Improved decision-making: Working memory is essential for making decisions, as it allows you to weigh the pros and cons of different options and to make informed choices.
-
Increased creativity: Working memory is also important for creativity, as it allows you to generate new ideas and to combine them in novel ways.
Conclusion
Working memory is a complex and essential cognitive system that plays a vital role in our everyday lives. By understanding how working memory works, we can take steps to improve our memory and use it more effectively.
Tables
Table 1: Capacity and Duration of Working Memory
| Capacity | Duration |
|---|---|
| 7 items | A few seconds |
Table 2: Functions of Working Memory
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Temporary storage | Stores information that is needed for ongoing cognitive tasks |
| Manipulation of information | Allows us to manipulate information in various ways |
| Control of attention | Helps us to control our attention and focus on the task at hand |
Table 3: Pain Points of Working Memory
| Pain Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Forgetting | We often forget things that we need to remember |
| Distraction | We are easily distracted by our surroundings |
Table 4: Benefits of Working Memory
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved memory | Can improve our ability to remember things, learn new information, and solve problems |
| Increased productivity | Can be more productive in our personal and professional lives |
| Reduced stress | Can reduce stress and improve our overall well-being |
| Improved decision-making | Can make better decisions |
| Increased creativity | Can generate new ideas and combine them in novel ways |