The period from 1750 to 1900 witnessed a remarkable surge in nationalism, a powerful force that reshaped the global political landscape. This ideology, characterized by a heightened sense of national identity and loyalty, played a pivotal role in shaping the development of nation-states, influencing political and social movements, and ultimately leading to major transformations in international relations.

Historical Context
The roots of nationalism can be traced back to the Enlightenment period, which emphasized the importance of reason, individual rights, and the social contract. In the 18th century, the American Revolution (1775-1783) and the French Revolution (1789-1799) became catalysts for the spread of nationalist sentiment, as people began to identify more strongly with their homelands than with their monarchies.
Political Implications
Nationalism had a profound impact on the political sphere. It inspired the formation of nation-states based on shared language, culture, and history. These nation-states sought to establish their own governments and territories, often through revolutions or wars of independence. The desire for self-determination and national unity became a driving force behind the rise of movements such as the Italian Risorgimento (1848-1871) and the German unification (1871).
Social and Cultural Impact
Nationalism not only influenced politics but also permeated social and cultural life. It fueled the growth of national pride and cultural expressions such as art, music, and literature. Writers and artists celebrated national heroes, myths, and traditions, while educational systems were used to promote a sense of national identity among citizens. The rise of nationalism also led to the emergence of movements for social equality and the rights of minority groups within nation-states.
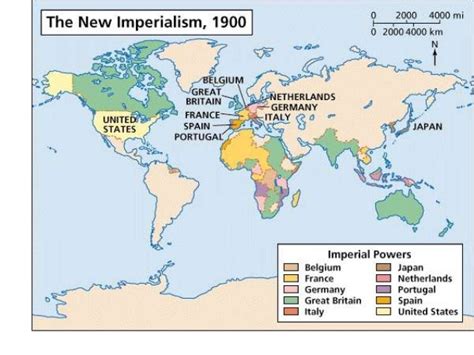
The Industrial Revolution and Imperialism
The Industrial Revolution of the 19th century contributed to the spread of nationalism. Economic growth and technological advancements created new industries and a more interconnected world, which in turn fostered a greater sense of national identity and competition among countries. The scramble for colonies and the rise of imperialism further intensified nationalist sentiments, as empires sought to expand their territories and influence.
The Rise of Mass Media
The development of mass media, such as newspapers and magazines, played a crucial role in fostering nationalism. These publications reached a wide audience and disseminated nationalistic ideas and propaganda, helping to shape public opinion and generate support for nationalist causes. The press was used to mobilize citizens, promote national unity, and challenge rival nations.
Consequences of Nationalism
The influence of nationalism was both positive and negative. It served as a powerful force for self-determination and national liberation, but it also had the potential to lead to conflict and division. The rise of extreme nationalist ideologies and the desire for territorial expansion often resulted in wars and persecution. The negative consequences of nationalism culminated in the outbreak of World War I in 1914, which devastated Europe and had far-reaching consequences for the global order.
Table 1: The Growth of Nationalism in Europe
| Country | Nationalist Revolution | Year |
|---|---|---|
| France | French Revolution | 1789-1799 |
| Italy | Risorgimento | 1848-1871 |
| Germany | German Unification | 1871 |
| Russia | October Revolution | 1917 |
| United Kingdom | Irish Home Rule Movement | 1880s-1914 |
| Austria-Hungary | Rise of Nationalism in Multiethnic Empire | 19th century |
Table 2: The Impact of Nationalism on Social and Cultural Life
| Aspect | Effects |
|---|---|
| Literature | Celebration of national heroes and mythologies |
| Art | Development of nationalist themes and symbols |
| Music | Composers inspired by national traditions |
| Education | Promotion of national identity and history |
| Social Movements | Demands for social equality and rights for minority groups |
Table 3: The Rise of Mass Media and Nationalism
| Type of Media | Role |
|---|---|
| Newspapers | Dissemination of nationalist ideas and propaganda |
| Magazines | Popularization of nationalistic literature and culture |
| Radio | Mobilization of citizens and promotion of national unity |
| Film | Creation of iconic images of national identity and history |
Table 4: The Consequences of Nationalism
| Positive Consequences | Negative Consequences |
|---|---|
| Self-determination and national liberation | Wars and conflict |
| National unity and pride | Extreme nationalist ideologies |
| Cultural expression and identity | Persecution of minority groups |
| Democratic movements | Rise of authoritarian regimes |
Conclusion
Nationalism played a pivotal role in shaping the world from 1750 to 1900. It fueled the formation of nation-states, influenced political and social movements, and had a profound impact on cultural life. While it served as a force for self-determination and national identity, it also had the potential to lead to conflict and division. The legacy of nationalism continues to shape international relations and the dynamics of national identity around the world.