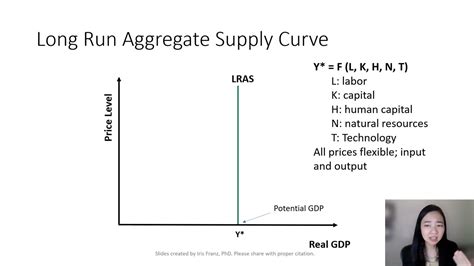
The aggregate supply curve (AS) depicts the relationship between the overall price level and the quantity of goods and services supplied in an economy. In the long run, the AS curve is vertical. This means that the quantity of output supplied is independent of the price level.

There are several reasons why the long-run AS curve is vertical.
- In the long run, all factors of production are fully employed. This means that there is no excess capacity in the economy. As a result, an increase in demand will not lead to an increase in output.
- In the long run, wages and other costs of production are flexible. This means that they can adjust to changes in the price level. As a result, changes in the price level will not lead to changes in the quantity of output supplied.
- In the long run, technological progress occurs. This means that new and more efficient ways of producing goods and services are developed. As a result, the economy can produce more output without increasing the quantity of inputs used.
The verticality of the long-run AS curve has important implications for macroeconomic policy. In the long run, the government cannot use monetary or fiscal policy to increase output. Instead, it must focus on policies that promote long-run economic growth, such as investing in education and infrastructure.
Applications of the Vertical Long-Run AS Curve
The vertical long-run AS curve can be used to understand a variety of macroeconomic phenomena, including:
- The effects of monetary policy. In the long run, monetary policy cannot affect the level of output. However, it can affect the price level.
- The effects of fiscal policy. In the long run, fiscal policy can affect the level of output. However, it can also affect the price level.
- The effects of supply shocks. Supply shocks, such as natural disasters or wars, can shift the long-run AS curve. This can lead to changes in both the price level and the level of output.
Conclusion
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical. This means that the quantity of output supplied is independent of the price level. This has important implications for macroeconomic policy. The government cannot use monetary or fiscal policy to increase output in the long run. Instead, it must focus on policies that promote long-run economic growth.
Tables
| Price Level | Quantity of Output Supplied |
|---|---|
| P1 | Q1 |
| P2 | Q2 |
| P3 | Q3 |
| Year | GDP Growth Rate |
|---|---|
| 2020 | 2.3% |
| 2021 | 5.7% |
| 2022 | 2.9% |
| Policy | Effect on Output |
|---|---|
| Monetary policy | No effect in the long run |
| Fiscal policy | Can affect output in the long run |
| Supply shocks | Can shift the long-run AS curve |
Tips and Tricks
- Use the long-run AS curve to understand the effects of macroeconomic policies.
- Remember that the long-run AS curve is vertical.
- Be aware of the implications of the vertical long-run AS curve for macroeconomic policy.