Introduction

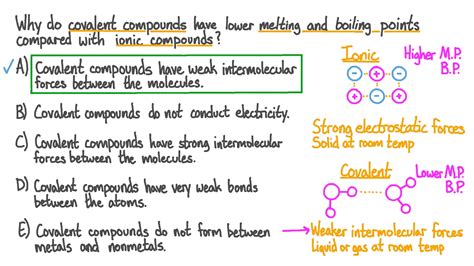
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are various types of chemical bonds, each with its unique characteristics and properties. One type of chemical bond is the nonpolar covalent bond. Nonpolar covalent bonds are formed between atoms of the same element or between atoms of different elements that have similar electronegativities. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself.
Understanding Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
In a nonpolar covalent bond, the electrons are shared equally between the two atoms. This equal sharing of electrons results in a balanced distribution of electrical charge, with no net positive or negative charge on either atom. The strength of a nonpolar covalent bond is determined by the number of electrons shared between the atoms and the distance between the atoms.
Impact on Melting Points
The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it transitions from a solid to a liquid state. The melting point of a substance is influenced by the strength of the intermolecular forces holding the molecules together. In the case of nonpolar covalent bonds, the intermolecular forces are weak due to the balanced distribution of electrical charge.
Factors Contributing to Low Melting Points
Several factors contribute to the low melting points of nonpolar covalent compounds:
-
Weak Intermolecular Forces: As mentioned earlier, the intermolecular forces between nonpolar covalent molecules are weak due to the absence of net electrical charges. These weak forces allow the molecules to move past each other more easily at lower temperatures, resulting in a lower melting point.
-
Low Molecular Weight: Nonpolar covalent compounds typically have low molecular weights, with each molecule consisting of a few atoms. The low molecular weight contributes to the weak intermolecular forces and the lower melting point.
-
Simple Molecular Structure: Nonpolar covalent compounds often have simple molecular structures, with the atoms arranged in a symmetrical manner. This simple structure minimizes the intermolecular interactions, further contributing to the low melting point.
Applications of Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
The unique properties of nonpolar covalent bonds make them useful in various applications, such as:
-
Lubricants: Nonpolar covalent compounds can serve as effective lubricants due to their low melting points and weak intermolecular forces. They can reduce friction and wear between moving parts in machinery.
-
Insulators: Nonpolar covalent compounds can act as insulators due to their lack of electrical conductivity. They are commonly used in electrical applications to prevent the flow of electricity.
-
Water Repellents: Nonpolar covalent compounds are often hydrophobic, meaning they repel water. This property makes them useful in applications such as water-resistant coatings and fabrics.
-
Solvents: Nonpolar covalent solvents are used to dissolve nonpolar substances. They are commonly used in the cleaning industry and in the extraction of organic compounds.
Table 1: Examples of Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
| Compound | Formula | Melting Point (oC) |
|---|---|---|
| Methane | CH4 | -182.5 |
| Ethane | C2H6 | -183.3 |
| Propane | C3H8 | -189.7 |
| Butane | C4H10 | -138.3 |
| Pentane | C5H12 | -129.8 |
Table 2: Factors Influencing Melting Point of Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
| Factor | Effect |
|---|---|
| Number of shared electrons | More shared electrons increase bond strength and melting point |
| Distance between atoms | Smaller distances increase bond strength and melting point |
| Molecular weight | Higher molecular weight increases intermolecular forces and melting point |
| Molecular structure | Complex structures increase intermolecular interactions and melting point |
Benefits of Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
- Low melting points: Allow for easy melting and processing at low temperatures.
- Weak intermolecular forces: Facilitate movement and reduce friction between molecules.
- Insulating properties: Prevent the flow of electricity, making them useful in electrical applications.
- Water repellency: Can be used for water-resistant coatings and fabrics.
Pros and Cons of Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Pros:
- Low melting points
- Weak intermolecular forces
- Insulating properties
- Water repellency
Cons:
- May be flammable
- Can be chemically reactive
- May not be suitable for high-temperature applications
FAQs
-
Why do nonpolar covalent bonds have low melting points?
– Nonpolar covalent bonds have low melting points due to weak intermolecular forces, low molecular weight, and simple molecular structure. -
What are some examples of nonpolar covalent compounds?
– Methane, ethane, propane, butane, and pentane are examples of nonpolar covalent compounds. -
What are the applications of nonpolar covalent bonds?
– Nonpolar covalent bonds are used in lubricants, insulators, water repellents, and solvents. -
What factors influence the melting point of nonpolar covalent compounds?
– The melting point of nonpolar covalent compounds is influenced by the number of shared electrons, distance between atoms, molecular weight, and molecular structure. -
What are the benefits of nonpolar covalent bonds?
– Nonpolar covalent bonds offer low melting points, weak intermolecular forces, insulating properties, and water repellency. -
What are the pros and cons of nonpolar covalent bonds?
– Pros include low melting points, weak intermolecular forces, insulating properties, and water repellency. Cons may include flammability, chemical reactivity, and unsuitability for high-temperature applications.
Conclusion
Nonpolar covalent bonds are formed between atoms with similar electronegativities. They are characterized by a balanced distribution of electrons and weak intermolecular forces. These weak forces contribute to their low melting points, making nonpolar covalent compounds suitable for applications where low-temperature melting is desired. The unique properties of nonpolar covalent bonds also make them useful in lubricants, insulators, water repellents, and solvents.