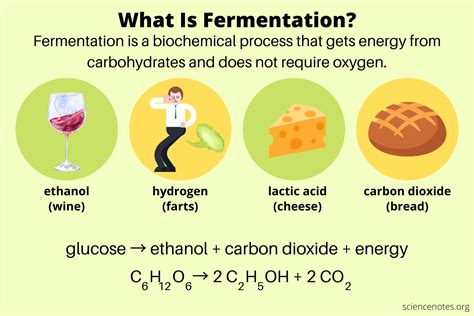
Fermentation reactions are essential for life on Earth. They provide cells with a source of energy and allow them to recycle waste products.

Energy Production
Fermentation is an anaerobic process, meaning that it does not require oxygen. This makes it a valuable energy source for cells that live in environments where oxygen is scarce, such as the deep ocean or the human gut.
Fermentation reactions produce ATP, the energy currency of cells. ATP is used to power all cellular activities, including growth, movement, and reproduction.
Waste Recycling
Fermentation reactions also help cells to recycle waste products. When cells break down glucose for energy, they produce waste products such as pyruvate and lactate. These waste products can be toxic to cells if they are not removed.
Fermentation reactions convert pyruvate and lactate into harmless products such as ethanol and carbon dioxide. These products can then be excreted from the cell.
Other Functions of Fermentation
In addition to energy production and waste recycling, fermentation reactions have a number of other important functions in cells. For example, fermentation reactions:
- Help to maintain the pH balance of cells
- Contribute to the flavor and aroma of foods and beverages
- Play a role in the immune response
Fermentation in Different Organisms
Fermentation reactions are found in a wide variety of organisms, including bacteria, yeast, and plants. Each organism uses fermentation to produce different products and for different purposes.
For example, bacteria use fermentation to produce lactic acid, which is used to make yogurt and cheese. Yeast use fermentation to produce ethanol, which is used to make beer and wine. Plants use fermentation to produce a variety of products, including ethanol, lactic acid, and acetic acid.
Importance of Fermentation Reactions
Fermentation reactions are essential for life on Earth. They provide cells with a source of energy, allow them to recycle waste products, and contribute to a variety of other important functions.
Without fermentation reactions, cells would not be able to survive and life on Earth would not be possible.
- Anaerobic: A process that does not require oxygen
- ATP: The energy currency of cells
- Fermentation: An anaerobic process that produces ATP and recycles waste products
- Pyruvate: A waste product of glucose breakdown
- Lactate: A waste product of glucose breakdown
- Ethanol: A product of fermentation
- Carbon dioxide: A product of fermentation
- What are fermentation reactions?
Fermentation reactions are anaerobic processes that produce ATP and recycle waste products.
- Why are fermentation reactions important?
Fermentation reactions are important because they provide cells with a source of energy and allow them to recycle waste products.
- What are some examples of fermentation reactions?
Some examples of fermentation reactions include the production of lactic acid by bacteria, the production of ethanol by yeast, and the production of acetic acid by plants.
- What are the products of fermentation reactions?
The products of fermentation reactions vary depending on the organism that is carrying out the reaction. Some common products of fermentation reactions include ethanol, lactic acid, acetic acid, and carbon dioxide.
- What are the applications of fermentation reactions?
Fermentation reactions are used in a wide variety of applications, including the production of food, beverages, and fuels.
| Organism | Product of Fermentation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Lactic acid | Yogurt, cheese |
| Yeast | Ethanol | Beer, wine |
| Plants | Ethanol, lactic acid, acetic acid | Food, beverages, fuels |
| Product of Fermentation | Organism | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | Yeast | Beer, wine, fuel |
| Lactic acid | Bacteria | Yogurt, cheese, food preservative |
| Acetic acid | Plants | Vinegar, food additive |
| Type of Fermentation | Organism | Product |
|---|---|---|
| Alcoholic fermentation | Yeast | Ethanol |
| Lactic acid fermentation | Bacteria | Lactic acid |
| Acetic acid fermentation | Plants | Acetic acid |
| Application of Fermentation | Product | Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Food production | Yogurt, cheese, bread | Food and beverage |
| Beverage production | Beer, wine, vinegar | Food and beverage |
| Fuel production | Ethanol, biodiesel | Energy |