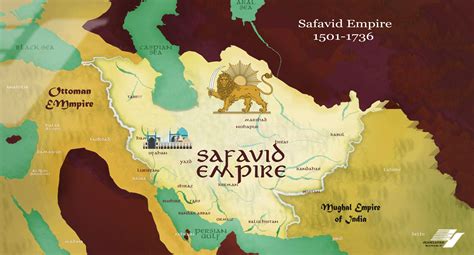
Origins and Rise to Power
The Safavids were a Shia Muslim dynasty that emerged in Persia (modern-day Iran) in the early 16th century. Founded by Ismail I, a charismatic Sufi mystic and military leader, they quickly established a vast empire that stretched from present-day Turkey to India.

Religious Policy: The Shia Revival
Under the Safavids, Persia underwent a profound religious transformation. Ismail I declared Shia Islam as the official state religion, making it the only recognized interpretation of Islam within their realm. This move significantly alienated the country’s majority Sunni population, leading to internal tensions and conflicts.
Cultural Legacy: The Golden Age of Persian Civilization
The Safavid era witnessed a flourishing of Persian culture, art, and architecture. Masterpieces such as the Shah Tahmasb Manuscript and the Isfahan Royal Mosque showcased the dynasty’s artistic patronage. Safavid poets like Hafiz and Saadi contributed to Persian literature’s enduring legacy.
Economic Innovations: The Silk Road and Trade
The Safavids revived and expanded the ancient Silk Road, a vital trade route connecting Europe and Asia. This enabled them to establish lucrative trade relationships with China, India, and the Ottoman Empire. The empire also benefited from Persia’s abundant natural resources, including copper, silver, and oil.
Political Structure: Centralization and Bureaucracy
The Safavids developed a centralized political system based on a powerful monarch. The emperor’s court governed through an elaborate bureaucracy that managed the empire’s vast territory. Provincial governors and military commanders were loyal to the king and enforced his authority.
Military Strength: The Qizilbash Warriors
The Safavid army’s core was the Qizilbash, a group of fierce warrior tribesmen who played a crucial role in the empire’s expansion and defense. Their devotion to Shia Islam and their distinctive red headgear gave them a distinct religious and military identity.
Decline and Fall
Despite their initial success, the Safavids faced increasing pressure from both internal and external forces. Domestic rebellions and conflicts with the Ottoman Empire weakened the empire. In the late 18th century, the Safavid dynasty collapsed due to a combination of political instability, economic decline, and foreign invasions.
Table 1: Safavid Rulers and Reigns
| Ruler | Reign |
|---|---|
| Ismail I | 1501-1524 |
| Tahmasp I | 1524-1576 |
| Ismail II | 1576-1578 |
| Muhammad Khodabanda | 1578-1588 |
| Abbas I | 1588-1629 |
| Safi | 1629-1642 |
| Abbas II | 1642-1666 |
| Suleiman I | 1666-1694 |
| Shah Hussain | 1694-1722 |
Table 2: Key Events in Safavid History
| Event | Date |
|---|---|
| Rise of Ismail I and establishment of Safavid dynasty | 1501 |
| Declaration of Shia Islam as the state religion | 1501 |
| Conquest of Baghdad | 1508 |
| Battle of Chaldiran (defeat by Ottomans) | 1514 |
| Reign of Abbas I and expansion of the empire | 1588-1629 |
| Construction of the Isfahan Royal Mosque | 1613 |
| Decline and collapse of Safavid dynasty | Late 18th century |
Table 3: Impact of Safavids on Persian Culture and Society
| Impact |
|—|—|
| Revival and promotion of Shia Islam |
| Patronage of Persian art, architecture, and literature |
| Establishment of a centralized state with an efficient bureaucracy |
| Expansion of trade and economic prosperity |
| Cultural exchange with neighboring empires and regions |
Table 4: Safavid Empire Facts and Statistics
| Fact | Statistic |
|---|---|
| Area of the empire at its height | Over 2.5 million square kilometers |
| Population | Estimated to be over 10 million |
| Official religion | Shia Islam |
| Ruling dynasty | Safavid |
| Key industries | Trade, agriculture, mining |
| Capital city | Isfahan |
FAQs
Q: Why were the Safavids significant?
A: The Safavids were a major power in the 16th and 17th centuries, controlling a vast empire and leaving a lasting legacy in Persian culture, art, and politics.
Q: What caused the decline of the Safavid Empire?
A: The Safavids faced a combination of domestic rebellions, conflicts with neighboring empires, economic problems, and political instability, leading to their eventual collapse.
Q: How did the Safavids impact Persian culture?
A: The Safavids revived and promoted Shia Islam, patronized Persian art and architecture, and encouraged cultural exchange with other regions.
Q: What were the Qizilbash?
A: The Qizilbash were a group of warrior tribesmen who formed the core of the Safavid army and played a crucial role in their military conquests.
Q: Who founded the Safavid dynasty?
A: Ismail I, a charismatic Sufi mystic and military leader, founded the Safavid dynasty in 1501.
Q: What was the significance of the Battle of Chaldiran?
A: The Battle of Chaldiran (1514) resulted in a defeat for the Safavids by the Ottoman Empire, marking a turning point in Safavid expansion and leading to a strategic shift in their foreign policy.
Q: Why did the Safavids declare Shia Islam as the state religion?
A: Ismail I’s declaration of Shia Islam as the official state religion was a deliberate move to distinguish the Safavid empire from the neighboring Sunni Ottoman Empire and assert their religious authority.
Q: What were the economic strengths of the Safavid Empire?
A: The Safavids benefited from their strategic location on the Silk Road, as well as their abundant natural resources, such as copper, silver, and oil, which contributed to their economic prosperity.