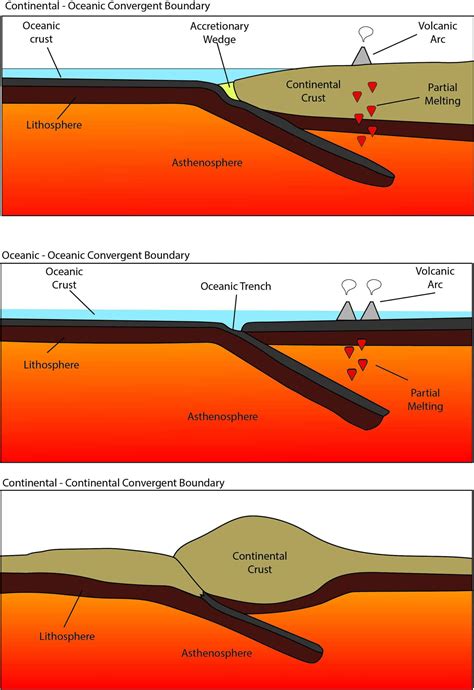
Convergent boundaries are regions where two or more tectonic plates collide. These boundaries are often associated with the formation of mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes.

There are three main types of convergent boundaries:
- Oceanic-continental convergence: This occurs when an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. The denser oceanic plate is subducted beneath the continental plate, causing the continental plate to uplift and form mountains. Examples of oceanic-continental convergent boundaries include the Andes Mountains and the Himalayas.
- Oceanic-oceanic convergence: This occurs when two oceanic plates collide. One plate is usually subducted beneath the other, causing the formation of a volcanic arc. Examples of oceanic-oceanic convergent boundaries include the Mariana Trench and the Tonga Trench.
- Continental-continental convergence: This occurs when two continental plates collide. The collision causes the plates to fold and uplift, forming mountain ranges. Examples of continental-continental convergent boundaries include the Alps and the Himalayas.
Characteristics of Convergent Boundaries
Convergent boundaries are characterized by the following features:
- Folding and thickening of the crust: The collision of two tectonic plates causes the crust to fold and thicken. This can lead to the formation of mountain ranges.
- Volcanism: The subduction of one tectonic plate beneath another can cause the formation of volcanoes. This is because the subducted plate releases water and other volatiles, which can cause the overlying plate to melt.
- Earthquakes: The collision of two tectonic plates can cause earthquakes. This is because the plates can become stuck, and when they finally move, they release a lot of energy.
Effects of Convergent Boundaries
Convergent boundaries can have a significant impact on the surrounding environment. These effects include:
- Mountain building: The collision of two tectonic plates can cause the formation of mountain ranges. These mountain ranges can have a significant impact on the climate and ecology of the surrounding region.
- Volcanism: The subduction of one tectonic plate beneath another can cause the formation of volcanoes. These volcanoes can be a hazard to human life and property, but they can also provide benefits such as geothermal energy and fertile soil.
- Earthquakes: The collision of two tectonic plates can cause earthquakes. These earthquakes can be a hazard to human life and property, but they can also provide information about the structure of the Earth’s interior.
Conclusion
Convergent boundaries are important regions of the Earth’s surface. They are responsible for the formation of mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. These features can have a significant impact on the surrounding environment and human life.