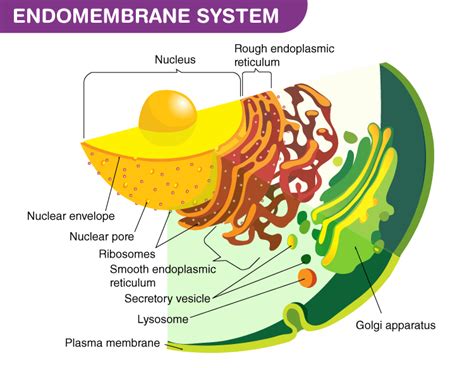
Endomembranes are a complex network of membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells. They play a crucial role in a wide range of cellular processes, including protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and detoxification.

There are several different types of endomembranes, each with its own unique function. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is responsible for protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The Golgi apparatus processes and modifies proteins and lipids before they are transported to their final destination. Lysosomes are responsible for digesting and recycling cellular waste products. Vacuoles are storage organelles that can contain a variety of materials, including nutrients, water, and waste products.
Endomembranes are essential for cell function. They provide a compartmentalized environment for cellular processes to occur and help to maintain cellular homeostasis.
Here are some statements that correctly describe an endomembrane function:
- The endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes proteins and lipids.
- The Golgi apparatus processes and modifies proteins and lipids.
- Lysosomes digest and recycle cellular waste products.
- Vacuoles store nutrients, water, and waste products.
Here is a table summarizing the functions of the different types of endomembranes:
| Endomembrane | Function |
|---|---|
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Protein synthesis and lipid metabolism |
| Golgi apparatus | Processing and modification of proteins and lipids |
| Lysosomes | Digestion and recycling of cellular waste products |
| Vacuoles | Storage of nutrients, water, and waste products |
Endomembranes are essential for human health. They play a role in a wide range of diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Cancer: Endomembranes are involved in the synthesis and secretion of proteins that are essential for cell growth and division. Mutations in genes that encode endomembrane proteins can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and cancer.
Diabetes: Endomembranes are involved in the production and secretion of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Mutations in genes that encode endomembrane proteins can lead to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Neurodegenerative disorders: Endomembranes are involved in the production and secretion of proteins that are essential for neuronal function. Mutations in genes that encode endomembrane proteins can lead to neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Endomembranes are essential for cell function and human health. They play a role in a wide range of cellular processes, including protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and detoxification. Mutations in genes that encode endomembrane proteins can lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.