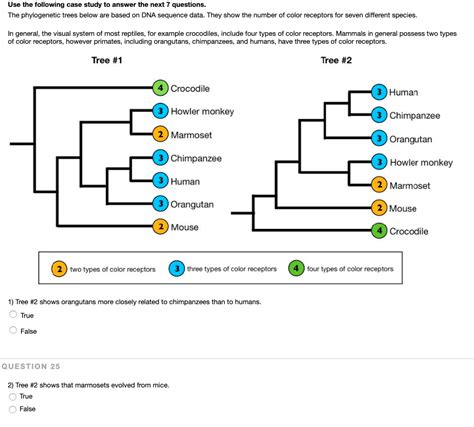
Phylogenetic trees are a powerful tool for understanding the evolutionary relationships between different species. They can be used to trace the origins of new species, identify common ancestors, and study the processes of evolution.

There are many different ways to construct a phylogenetic tree, but they all share some common features. First, they start with a group of species that are known to be related. Then, the tree is built by adding branches to connect the species in a way that reflects their evolutionary history. The length of each branch represents the amount of time that has passed since the two species connected by that branch diverged from a common ancestor.
Phylogenetic trees can be used to answer a wide range of questions about evolution. For example, they can be used to:
- Trace the origins of new species
- Identify common ancestors
- Study the processes of evolution
- Understand the impact of environmental change on species
Phylogenetic trees are an essential tool for evolutionary biologists. They provide a visual representation of the evolutionary relationships between different species, and they can be used to answer a wide range of questions about evolution.
Phylogenetic trees are constructed using a variety of methods, but the most common method is called cladistics. Cladistics is a method of classifying organisms based on their shared derived characters. A derived character is a character that is present in a group of organisms but not in their ancestors.
To construct a cladogram, scientists first identify the outgroup, which is a species that is closely related to the group of species being studied but is not a member of that group. The outgroup is used as a reference point for determining which characters are derived.
Once the outgroup has been identified, scientists examine the characters of the species being studied and identify the shared derived characters. These characters are then used to construct a tree that shows the evolutionary relationships between the species.
Phylogenetic trees are a powerful tool for understanding evolution, but they also have some limitations. One limitation is that they are only as accurate as the data that they are based on. If the data is incomplete or inaccurate, the tree will be inaccurate.
Another limitation is that phylogenetic trees can only show the evolutionary relationships between species that are closely related. They cannot be used to show the relationships between species that are very distantly related.
Finally, phylogenetic trees cannot be used to predict the future. They can only show the evolutionary relationships between species as they are currently understood.
Phylogenetic trees have a wide range of applications in biology. They can be used to:
- Trace the origins of new species
- Identify common ancestors
- Study the processes of evolution
- Understand the impact of environmental change on species
- Develop new drugs and treatments
- Conserve endangered species
Phylogenetic trees are an essential tool for biologists. They provide a visual representation of the evolutionary relationships between different species, and they can be used to answer a wide range of questions about evolution.
Here are some tips for creating phylogenetic trees:
- Start with a good dataset. The data you use to construct your tree will have a significant impact on the accuracy of your tree. Make sure that your data is complete, accurate, and up-to-date.
- Choose the right method for constructing your tree. There are many different methods for constructing phylogenetic trees. The best method for you will depend on the size of your dataset, the type of data you have, and the level of accuracy you need.
- Be aware of the limitations of phylogenetic trees. Phylogenetic trees are a powerful tool, but they also have some limitations. Be aware of these limitations and interpret your tree accordingly.
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when creating phylogenetic trees:
- Using incomplete or inaccurate data. This is one of the most common mistakes that people make when creating phylogenetic trees. Make sure that your data is complete, accurate, and up-to-date.
- Choosing the wrong method for constructing your tree. There are many different methods for constructing phylogenetic trees. The best method for you will depend on the size of your dataset, the type of data you have, and the level of accuracy you need.
- Interpreting your tree incorrectly. Phylogenetic trees are a visual representation of the evolutionary relationships between different species. Make sure that you understand how to interpret your tree before you draw any conclusions.
Phylogenetic trees are a powerful tool for understanding evolution. They can be used to trace the origins of new species, identify common ancestors, study the processes of evolution, and understand the impact of environmental change on species.
By following these tips, you can create accurate and informative phylogenetic trees.