Introduction
Acids and bases are two of the most important concepts in chemistry. They play a vital role in many chemical reactions, and they have a wide range of applications in everyday life. In this article, we will discuss the Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases, and we will provide examples of Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reactions.

Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory
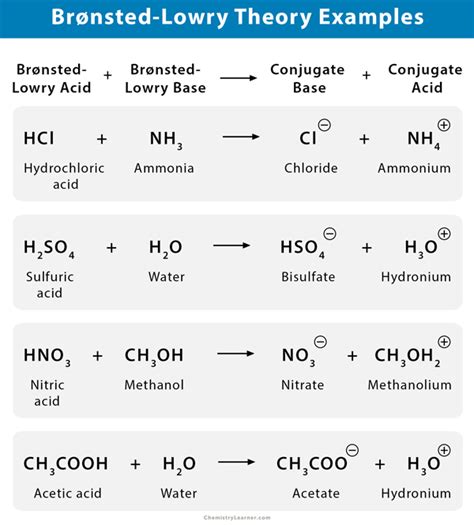
The Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases was developed by the Danish chemist Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and the English chemist Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. This theory defines an acid as a substance that can donate a proton (H+), and a base as a substance that can accept a proton.
According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory, an acid-base reaction is a reaction in which a proton is transferred from an acid to a base. The acid becomes a conjugate base, and the base becomes a conjugate acid.
Examples of Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Reactions
There are many different types of Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reactions. Some of the most common examples include:
- Neutralization reactions are reactions between an acid and a base that produce a salt and water. For example, the reaction of hydrochloric acid (HCl) with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) produces sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O).
- Acid-base titrations are used to determine the concentration of an acid or a base. In an acid-base titration, a known volume of acid is added to a known volume of base, and the pH of the solution is monitored. The equivalence point is the point at which the moles of acid and base are equal, and the pH of the solution is 7.
- Buffer solutions are solutions that resist changes in pH. Buffer solutions are made up of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Buffer solutions are used in a variety of applications, such as maintaining the pH of blood and urine.
Applications of Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases have a wide range of applications in everyday life. Some of the most common applications include:
- Batteries use acids and bases to generate electricity.
- Fertilizers use acids and bases to provide nutrients for plants.
- Food uses acids and bases to flavor and preserve food.
- Medicine uses acids and bases to treat a variety of diseases.
Conclusion
Acids and bases are two of the most important concepts in chemistry. They play a vital role in many chemical reactions, and they have a wide range of applications in everyday life. The Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases is a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of acids and bases.
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when working with Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases:
- Do not confuse acids with bases. Acids donate protons, while bases accept protons.
- Do not confuse conjugate acids with conjugate bases. The conjugate acid of a base is the acid that is formed when the base accepts a proton. The conjugate base of an acid is the base that is formed when the acid donates a proton.
- Do not use the terms “strong” and “weak” to describe acids and bases. Acids and bases are classified as strong or weak based on their degree of ionization. A strong acid ionizes completely in water, while a weak acid ionizes only partially. A strong base ionizes completely in water, while a weak base ionizes only partially.