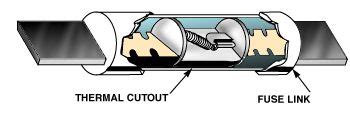
A dual element fuse is a type of electrical fuse that contains two separate fusible elements. These elements are connected in series, meaning that the current must pass through both elements in order to complete the circuit. If either element melts, the fuse will open, interrupting the flow of current. This helps to provide a higher level of protection against short circuits and overloads.

Dual element fuses typically consist of a low-melting-point element and a high-melting-point element. The low-melting-point element is designed to melt and open the circuit quickly in the event of a short circuit. The high-melting-point element is designed to melt and open the circuit more slowly in the event of an overload. This time-delay action helps to prevent nuisance tripping of the fuse.
Dual element fuses offer a number of advantages over single element fuses, including:
- Higher level of protection against short circuits and overloads
- Time-delay action prevents nuisance tripping
- Can be used in high-current applications
- Compact size
Dual element fuses are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Electrical panels
- Motor circuits
- Lighting circuits
- Appliance circuits
- Automotive circuits
When selecting a dual element fuse, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Amperage rating: The amperage rating of the fuse should be equal to or greater than the maximum current that will flow through the circuit.
- Voltage rating: The voltage rating of the fuse should be equal to or greater than the voltage of the circuit.
- Time-delay: The time-delay of the fuse should be appropriate for the application. A fast-acting fuse will open the circuit quickly in the event of a short circuit, while a slow-acting fuse will open the circuit more slowly in the event of an overload.
- Size: The size of the fuse should be appropriate for the fuse holder.
There are a few common mistakes that should be avoided when using dual element fuses. These mistakes include:
- Using a fuse with an amperage rating that is too low. This can cause the fuse to blow prematurely.
- Using a fuse with a voltage rating that is too low. This can cause the fuse to fail catastrophically.
- Using a fuse with an inappropriate time-delay. This can cause the fuse to either open the circuit too quickly or too slowly.
- Installing the fuse incorrectly. This can cause the fuse to make poor contact with the fuse holder, which can lead to arcing and overheating.
Dual element fuses are a versatile and reliable type of electrical fuse that offer a high level of protection against short circuits and overloads. By following the tips and tricks outlined in this article, you can select and use dual element fuses safely and effectively.
- What is the difference between a dual element fuse and a single element fuse?
A dual element fuse contains two separate fusible elements, while a single element fuse contains only one fusible element. This gives dual element fuses a higher level of protection against short circuits and overloads.
- What is the time-delay action of a dual element fuse?
The time-delay action of a dual element fuse is the amount of time it takes for the fuse to open the circuit after it has melted. This time-delay helps to prevent nuisance tripping of the fuse.
- How do I select the correct dual element fuse for my application?
When selecting a dual element fuse, you should consider the amperage rating, voltage rating, time-delay, and size of the fuse. You should also consider the specific application for which the fuse will be used.
- What are some common mistakes to avoid when using dual element fuses?
Some common mistakes to avoid when using dual element fuses include using a fuse with an amperage rating that is too low, using a fuse with a voltage rating that is too low, using a fuse with an inappropriate time-delay, and installing the fuse incorrectly.
| Table 1: Amperage Ratings of Dual Element Fuses | Table 2: Voltage Ratings of Dual Element Fuses |
|---|---|
| 1 amp | 250 volts |
| 2 amps | 400 volts |
| 3 amps | 600 volts |
| 4 amps | 800 volts |
| 5 amps | 1000 volts |
| Table 3: Time-Delays of Dual Element Fuses | Table 4: Sizes of Dual Element Fuses |
|---|---|
| Fast-acting | 1/4 inch x 1 1/4 inches |
| Slow-acting | 1/4 inch x 1 3/8 inches |
| Ultra-slow-acting | 1/4 inch x 2 inches |
| Non-delay | 1/4 inch x 2 1/4 inches |