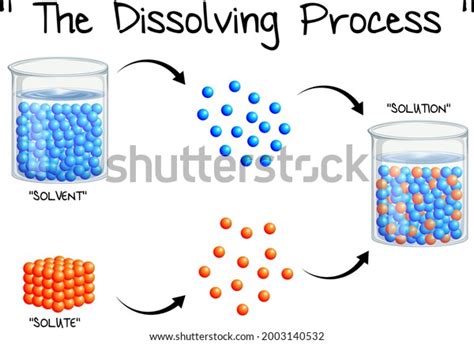
When it comes to dissolving a substance, there are two main steps involved:

- Wetting: This is the process of getting the solvent (the liquid that you’re dissolving the substance in) to come into contact with all of the surface area of the solute (the substance that you’re dissolving).
- Diffusion: This is the process of the solute molecules spreading out through the solvent.
The second step, diffusion, is what actually causes the solute to dissolve. As the solute molecules spread out, they become surrounded by solvent molecules and are no longer able to interact with each other. This causes the solute to break down into individual molecules, which are then able to be dispersed throughout the solvent.
The rate of diffusion is determined by a number of factors, including:
- The temperature of the solvent: The higher the temperature, the faster the diffusion rate.
- The concentration of the solute: The higher the concentration of the solute, the slower the diffusion rate.
- The size of the solute molecules: The larger the solute molecules, the slower the diffusion rate.
How to Increase the Rate of Diffusion
There are a number of things that you can do to increase the rate of diffusion, including:
- Stirring the solution: Stirring the solution will help to distribute the solute molecules more evenly throughout the solvent.
- Heating the solution: Heating the solution will increase the temperature of the solvent, which will in turn increase the diffusion rate.
- Adding a surfactant: A surfactant is a substance that helps to reduce the surface tension of the solvent. This will make it easier for the solvent to come into contact with the solute molecules and increase the diffusion rate.
Applications of Diffusion
Diffusion is a very important process in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Dissolving solids in liquids: Diffusion is the process that allows solids to dissolve in liquids. This is a very important process in a variety of applications, such as cooking, cleaning, and manufacturing.
- Gas exchange in the lungs: Diffusion is the process that allows oxygen to move from the lungs into the bloodstream. This is a very important process for keeping us alive!
- Drug delivery: Diffusion is the process that allows drugs to move from the bloodstream into the cells of the body. This is a very important process for treating diseases and injuries.
Tips and Tricks
Here are a few tips and tricks for increasing the rate of diffusion:
- Use a solvent that is a good match for the solute. The more similar the solvent and solute are, the faster the diffusion rate will be.
- Use a higher concentration of solvent. The more solvent you use, the faster the diffusion rate will be.
- Stir the solution frequently. Stirring the solution will help to distribute the solute molecules more evenly throughout the solvent.
- Heat the solution. Heating the solution will increase the temperature of the solvent, which will in turn increase the diffusion rate.
- Add a surfactant. A surfactant is a substance that helps to reduce the surface tension of the solvent. This will make it easier for the solvent to come into contact with the solute molecules and increase the diffusion rate.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between wetting and diffusion?
A: Wetting is the process of getting the solvent to come into contact with all of the surface area of the solute. Diffusion is the process of the solute molecules spreading out through the solvent.
Q: What factors affect the rate of diffusion?
A: The rate of diffusion is affected by the temperature of the solvent, the concentration of the solute, and the size of the solute molecules.
Q: How can I increase the rate of diffusion?
A: You can increase the rate of diffusion by stirring the solution, heating the solution, adding a surfactant, or using a solvent that is a good match for the solute.
Conclusion
Diffusion is a very important process in a wide variety of applications. By understanding the factors that affect the rate of diffusion, you can use this process to your advantage.