The Bantu are a group of peoples who speak Bantu languages and share a common ancestry. They originated in Central Africa and have spread throughout much of the continent. Today, they make up the majority of the population in many African countries, including South Africa, Nigeria, Kenya, and Tanzania.

Bantu Origins
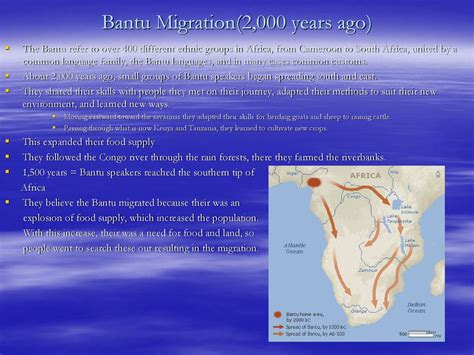
The Bantu are thought to have originated in the area of Cameroon and Nigeria around 3,000-4,000 years ago. They were likely farmers who practiced a slash-and-burn form of agriculture. As the population grew, the Bantu began to migrate in search of new land.
Bantu Migrations
The Bantu migrations were a series of movements that took place over several centuries. They were caused by a number of factors, including population pressure, warfare, and the search for new resources. The Bantu migrants traveled in large groups, often numbering in the thousands. They carried with them their crops, livestock, and tools.
The Bantu migrations had a profound impact on African history. They introduced new agricultural techniques and technologies to many parts of the continent. They also helped to spread the Bantu languages and cultures. By the 16th century, the Bantu had settled in much of sub-Saharan Africa.
Bantu Kingdoms
The Bantu migrations led to the establishment of a number of new kingdoms in Africa. These kingdoms were often organized around a central ruler who controlled a large territory. The most famous of these kingdoms was the Kingdom of Kongo, which flourished in Central Africa from the 14th to the 19th centuries. The Kingdom of Kongo was a wealthy and powerful state that had a significant impact on the development of West Africa.
Bantu Culture
The Bantu share a number of cultural similarities, including their languages, their agricultural practices, and their social organization. The Bantu languages are a group of closely related languages that are spoken by over 200 million people in Africa. The Bantu languages are tonal languages, which means that the pitch of the voice is used to distinguish different words.
The Bantu are primarily farmers who grow a variety of crops, including yams, cassava, and maize. They also raise livestock, such as cattle, goats, and sheep. The Bantu social organization is based on the extended family. The extended family is a group of relatives who live together and share resources.
Bantu History Today
The Bantu peoples have played a major role in African history. They have contributed to the continent’s agriculture, culture, and politics. Today, the Bantu continue to be a vital part of African society.
The Future of the Bantu
The future of the Bantu is uncertain. They face a number of challenges, including poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. However, the Bantu are a resilient people who have overcome many challenges in the past. They are likely to continue to play a major role in African history in the years to come.
Tables
| Bantu Language | Number of Speakers | Countries Spoken In |
|---|---|---|
| Swahili | 150 million | Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo, Mozambique |
| Zulu | 12 million | South Africa, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Mozambique |
| Yoruba | 30 million | Nigeria, Benin, Togo, Ghana |
| Amharic | 22 million | Ethiopia, Eritrea |
| Bantu Kingdom | Location | Dates |
|---|---|---|
| Kingdom of Kongo | Central Africa | 14th-19th centuries |
| Kingdom of Benin | West Africa | 13th-19th centuries |
| Kingdom of Ashanti | West Africa | 17th-19th centuries |
| Kingdom of Loango | Central Africa | 15th-19th centuries |
| Bantu Agricultural Practices | Crops Grown | Livestock Raised |
|---|---|---|
| Slash-and-burn agriculture | Yams, cassava, maize | Cattle, goats, sheep |
| Terrace farming | Rice, wheat, barley | Chickens, pigs |
| Irrigation farming | Tomatoes, onions, peppers | Cows, buffaloes |
| Bantu Social Organization | Structure | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Extended family | Elders are respected, children are cherished | Cooperation, community |
| Clan | People with a common ancestor | Loyalty, unity |
| Tribe | People who share a common language and culture | Patriotism, tradition |