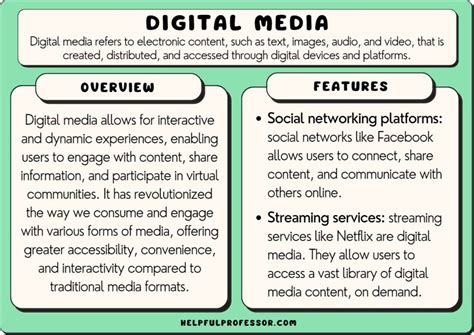
Specifications in digital media refer to the technical characteristics and requirements that define the capabilities and performance of digital devices, content, and platforms. They provide detailed information on the hardware, software, and network parameters necessary for optimal user experience and compatibility.

Key Specifications in Digital Media
1. Resolution
Resolution refers to the number of pixels used to display an image or video. Higher resolutions result in sharper and more detailed images, but they also require more storage space and processing power. Common resolution standards include:
- Standard Definition (SD): 720 x 480 pixels
- High Definition (HD): 1280 x 720 pixels
- Full High Definition (FHD): 1920 x 1080 pixels
- Ultra-High Definition (UHD/4K): 3840 x 2160 pixels
- 8K: 7680 x 4320 pixels
2. Frame Rate
Frame rate is the number of frames displayed per second in a video. Higher frame rates result in smoother and more fluid motion, while lower frame rates can cause choppiness. Common frame rates include:
- 24 fps (frames per second): Standard for movies and television
- 30 fps: Common for streaming video and gaming
- 60 fps: Desired for high-quality video and gaming
- 120 fps and higher: Used for ultra-smooth video and virtual reality applications
3. Bitrate
Bitrate refers to the amount of data transferred per second in a digital media file. Higher bitrates result in better video and audio quality, but they also increase file size. Common bitrate ranges include:
- Low bitrate (0-500 kbps): Suitable for streaming video on low-quality connections
- Medium bitrate (500-1500 kbps): Ideal for most streaming video applications
- High bitrate (1500-6000 kbps): Provides excellent video and audio quality for Blu-ray discs and high-end streaming
4. File Formats
File formats determine the way digital media is stored and compressed. Different formats have different advantages and compatibility with various devices and platforms. Common file formats include:
- JPEG: Image format with lossy compression, suitable for photographs
- PNG: Image format with lossless compression, suitable for graphics and logos
- MP4: Video format with lossy compression, widely used for streaming and playback
- MOV: Video format developed by Apple, offers high-quality video with efficient compression
- AVI: Video format developed by Microsoft, supports various codecs and resolutions
5. Audio Codecs
Audio codecs encode and decode audio data, determining the quality and file size of audio files. Common audio codecs include:
- MP3: Lossy audio codec, widely used for music streaming and downloads
- AAC: Advanced audio codec, offers higher quality than MP3 with similar file size
- FLAC: Lossless audio codec, provides the highest audio quality but with larger file sizes
Why Specifications Matter
Understanding specifications is crucial because it allows you to:
- Select the right devices and content: Specifications help you match the capabilities of your devices with the requirements of the content you want to consume.
- Ensure compatibility: Specifications ensure that your devices, software, and platforms are compatible with the media you want to access.
- Maximize user experience: By choosing devices and content that meet the appropriate specifications, you can ensure optimal playback quality, minimize buffering, and enhance your overall user experience.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring specifications: Assuming that all digital media is created equal can lead to compatibility issues and unsatisfactory user experiences.
- Overspending on unnecessary specifications: Purchasing devices or content with specifications that exceed your actual needs can be wasteful and unnecessary.
- Misinterpreting specifications: Not understanding the significance of different specifications can lead to incorrect decisions and subpar experiences.
Tips and Tricks
- Consider your intended use: Determine the primary purpose of the device or content you need to select specifications accordingly.
- Research and compare: Read reviews, consult with experts, and compare specifications of different options to make informed decisions.
- Prioritize essential specifications: Identify the specifications that are most important for your intended use and focus on meeting those requirements.
- Be flexible: Understand that specifications are guidelines, and slight variations may still provide satisfactory performance depending on your specific needs.
- Ask questions: Don’t hesitate to reach out to manufacturers, retailers, or online communities for clarification or advice on specifications.
By understanding and considering specifications in digital media, you can make informed choices that optimize your user experience and ensure compatibility and satisfaction with your devices and content.