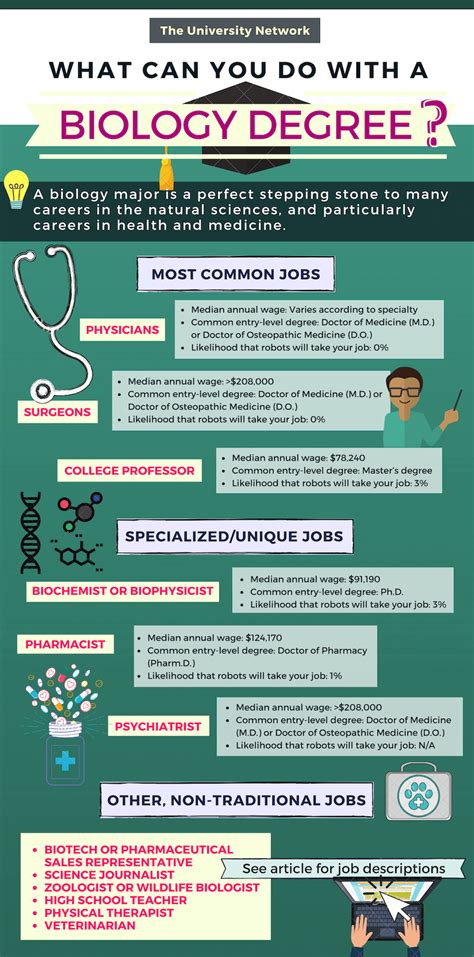
Introduction

Biology is a vast and ever-evolving field that offers a multitude of career opportunities. With a biology degree, you can pursue careers in healthcare, research, education, and various industries. This article will explore the diverse range of jobs available to individuals with a biology degree.
Healthcare
-
Physician: Physicians diagnose and treat diseases, injuries, and other health conditions. They typically hold a medical degree (MD) or a doctor of osteopathic medicine (DO).
-
Nurse: Nurses provide direct patient care, including administering medications, monitoring vital signs, and assisting with procedures. They typically hold an associate’s degree or a bachelor’s degree in nursing.
-
Physician assistant: Physician assistants are healthcare professionals who work under the supervision of a physician. They can perform physical exams, prescribe medications, and assist with surgeries. They typically hold a master’s degree in physician assistant studies.
-
Medical technologist: Medical technologists analyze patient samples, such as blood, tissue, and urine, to provide information for diagnosis and treatment. They typically hold a bachelor’s degree in medical technology.
-
Pharmacist: Pharmacists dispense medications and provide patient counseling on drug use. They typically hold a doctor of pharmacy (PharmD) degree.
Research
-
Biochemist: Biochemists study the chemical processes that occur in living organisms. They conduct experiments to understand how these processes contribute to health and disease.
-
Molecular biologist: Molecular biologists study the structure and function of genes and molecules. They conduct experiments to investigate the genetic basis of diseases and develop new treatments.
-
Cell biologist: Cell biologists study the structure and function of cells. They investigate how cells divide, grow, and interact with each other.
-
Microbiologist: Microbiologists study microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. They investigate how these organisms cause diseases and develop strategies to prevent and treat infections.
-
Zoologist: Zoologists study animals, including their behavior, habitat, and evolution. They conduct field and laboratory research to understand the diversity and ecology of animal species.
Education
-
Biology teacher: Biology teachers teach biology concepts to high school or college students. They typically hold a bachelor’s degree in biology or a related field and a teaching certification.
-
Science writer: Science writers communicate scientific information to the public through articles, books, and other media. They typically hold a bachelor’s degree in biology or a related field and strong writing skills.
-
Museum educator: Museum educators develop and deliver educational programs for visitors to museums and other cultural institutions. They typically hold a bachelor’s degree in biology or a related field and experience in museum education.
-
Science policy analyst: Science policy analysts advise policymakers on the scientific aspects of public policy issues. They typically hold a bachelor’s degree in biology or a related field and a graduate degree in public policy or a similar field.
Industries
-
Biotechnology: Biotechnology companies use biological systems to develop new products and technologies. They employ individuals with expertise in biology, chemistry, and engineering.
-
Pharmaceutical industry: Pharmaceutical companies develop and manufacture drugs and other therapies. They employ individuals with expertise in biology, chemistry, and pharmacology.
-
Food industry: Food companies use biological principles to develop new products and ensure food safety. They employ individuals with expertise in microbiology, food science, and nutrition.
-
Environmental consulting: Environmental consulting firms provide services to businesses and governments to help them comply with environmental regulations. They employ individuals with expertise in biology, environmental science, and engineering.
-
Wildlife management: Wildlife management agencies work to conserve and manage wildlife populations. They employ individuals with expertise in biology, ecology, and wildlife management.
New Applications
In addition to the traditional jobs listed above, there are emerging applications for biology degrees in new and innovative fields. These include:
-
Bioinformatics: Bioinformatics uses computational tools to analyze biological data. It has applications in drug discovery, disease diagnosis, and personalized medicine.
-
Synthetic biology: Synthetic biology involves designing and engineering new biological systems. It has the potential to create new drugs, materials, and energy sources.
-
Biostatistics: Biostatistics uses statistical methods to analyze biological data. It is essential for clinical trials, epidemiological studies, and public health research.
-
Biomimicry: Biomimicry involves imitating the designs and processes found in nature to solve human problems. It has applications in engineering, materials science, and architecture.
Job Outlook and Salaries
The job outlook for biologists is generally positive. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment of biological scientists will grow 6% from 2021 to 2031, faster than the average for all occupations.
Salaries for biologists vary depending on their level of education, experience, and industry. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for biological scientists in May 2021 was $93,010. The highest-paid 10% of biological scientists earned more than $157,680, while the lowest-paid 10% earned less than $49,630.
How to Choose the Right Job for You
Choosing the right job for you depends on your interests, skills, and career goals. Consider the following factors when making a decision:
- What are your interests? What aspects of biology interest you the most? Do you enjoy studying the human body, animals, or plants? Are you interested in research, healthcare, or industry?
- What are your skills? What skills do you have that are relevant to biology? Do you have strong analytical, problem-solving, or communication skills? Are you proficient in laboratory techniques or statistical analysis?
- What are your career goals? What do you want to achieve in your career? Do you want to become a doctor, a researcher, or work in industry? Are you interested in management, consulting, or entrepreneurship?
Tips for Finding a Job
Once you have chosen a career path, you can start looking for a job. Here are some tips:
- Network: Attend industry events, conferences, and career fairs. Meet with people in your field and learn about job opportunities.
- Use job boards: Search for jobs on websites such as LinkedIn, Indeed, and Monster.com.
- Contact companies directly: Reach out to companies that you are interested in working for and inquire about job openings.
- Tailor your resume and cover letter: Customize your resume and cover letter to each job you apply for. Highlight your skills and experience that are relevant to the position.
- Prepare for interviews: Practice answering common interview questions. Be prepared to talk about your experience, skills, and career goals.
Conclusion
A biology degree opens up a world of career opportunities. By exploring the diverse range of jobs available, you can find a career that matches your interests, skills, and career goals. With hard work and dedication, you can make a significant contribution to the field of biology and make a positive impact on the world.
Effective Strategies for Finding a Job with a Biology Degree
1. Define your goals and interests.
What are your career aspirations? What specific areas of biology interest you? Knowing your goals and interests will help you narrow down your job search and focus on positions that align with your passions.
2. Network and build relationships.
Attend industry events, conferences, and workshops to connect with professionals in your field. Join professional organizations and engage on LinkedIn to expand your network and learn about potential job opportunities.
3. Tailor your resume and cover letter.
Customize your resume and cover letter to each job you apply for. Highlight your skills and experience that are relevant to the position, and provide specific examples of your accomplishments.
4. Practice your interviewing skills.
Research common interview questions and prepare your answers. Practice your delivery and body language to ensure you make a confident and positive impression.
5. Explore different job search methods.
Utilize online job boards, company websites, and networking to find potential job openings. Consider contacting companies directly to inquire about any unadvertised positions.
Why a Biology Degree Matters
1. Strong foundation in science
Biology graduates possess a deep understanding of scientific principles and research methodologies. This foundation enables them to analyze complex data, solve problems, and make informed decisions.
2. Versatility
Biology graduates are versatile and adaptable professionals. They can pursue careers in research, healthcare, education, industry, and various other fields.
3. Critical thinking and problem-solving skills
Biology coursework develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for success in any profession. Graduates learn to analyze data, formulate hypotheses, and design experiments to find solutions.
4. Communication and interpersonal skills
Biologists often work in collaborative environments and present their research findings to diverse audiences. They develop strong communication and interpersonal skills that enhance their effectiveness in any career.
5. Career advancement
A biology degree provides a solid platform for career advancement. Graduates can pursue advanced degrees, such as master’s or doctoral degrees, to specialize in specific areas and enhance their marketability.
Benefits of a Biology Degree
1. Career flexibility
A biology degree opens doors to a wide range of career options, allowing individuals to explore different interests and pursue careers that align with their passions.
2. High earning potential
Biologists with advanced degrees, such as doctorates, can earn competitive salaries in research, academia, and industry.
3. Job security
Biology is a growing field with a high demand for professionals. Biologists are employed in various sectors,