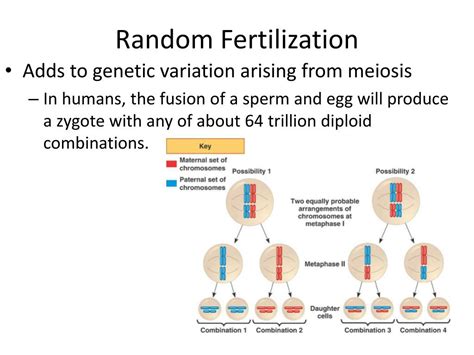
Random fertilization is a type of reproduction in which the sperm and egg that combine to create a new individual are chosen randomly from a pool of available gametes. This is in contrast to non-random fertilization, in which the sperm and egg that combine are chosen based on specific criteria, such as their genetic compatibility.

Random fertilization is the most common type of reproduction in animals, including humans. It is also found in some plants and fungi. The main advantage of random fertilization is that it increases the genetic diversity of a population, which can help to prevent the spread of disease and increase the chances of survival in a changing environment.
How Does Random Fertilization Work?
In random fertilization, the sperm and egg that combine to create a new individual are chosen randomly from a pool of available gametes. This pool of gametes may come from a single individual (self-fertilization) or from multiple individuals (cross-fertilization).
In humans, the pool of available gametes is created during meiosis, a process that divides a cell into four daughter cells, each of which contains half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. These daughter cells are then released into the body, where they can combine with gametes from other individuals to create new individuals.
Benefits of Random Fertilization
There are several benefits to random fertilization, including:
- Increased genetic diversity: Random fertilization increases the genetic diversity of a population, which can help to prevent the spread of disease and increase the chances of survival in a changing environment.
- Reduced risk of inbreeding: Random fertilization reduces the risk of inbreeding, which can lead to genetic disorders and other health problems.
- Increased chances of finding a compatible mate: Random fertilization increases the chances of finding a compatible mate, which can lead to successful reproduction and the production of healthy offspring.
Drawbacks of Random Fertilization
There are also some drawbacks to random fertilization, including:
- Increased risk of genetic disorders: Random fertilization can increase the risk of genetic disorders, such as sickle cell anemia and cystic fibrosis. This is because it is possible for two individuals with the same genetic disorder to produce a child who inherits two copies of the defective gene.
- Reduced fitness: Random fertilization can reduce the fitness of a population, as it can lead to the production of individuals who are not well-adapted to their environment. This is because it is possible for two individuals with different adaptations to produce a child who inherits a combination of traits that is not optimal for survival.
Examples of Random Fertilization
Random fertilization is found in a wide variety of organisms, including:
- Animals: Most animals, including humans, use random fertilization to reproduce.
- Plants: Some plants, such as corn and wheat, use random fertilization to reproduce.
- Fungi: Some fungi, such as mushrooms and yeast, use random fertilization to reproduce.
Applications of Random Fertilization
Random fertilization has a number of applications, including:
- Agriculture: Random fertilization can be used to create new varieties of crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases.
- Medicine: Random fertilization can be used to create new treatments for genetic disorders.
- Conservation: Random fertilization can be used to help preserve endangered species.
Conclusion
Random fertilization is a type of reproduction that has both benefits and drawbacks. It is important to understand how random fertilization works and its potential effects before deciding whether or not to use it.