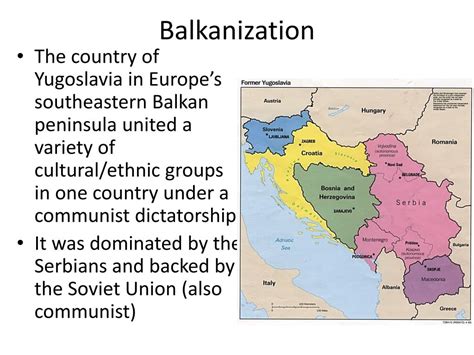
Balkanization, a term coined in the 19th century, refers to the fragmentation of a region into smaller, often hostile, and ethnically or culturally distinct states. Historically, the Balkan Peninsula has been a prime example of this process. However, Balkanization can occur in any region where there is a lack of national unity and a desire for autonomy among different groups.

Causes of Balkanization
- Ethnic and cultural diversity: The presence of multiple ethnic and cultural groups within a region can lead to tensions and conflicts if they are not adequately accommodated.
- Historical grievances: Past injustices and conflicts can create resentment and a desire for separation among different groups.
- Weak central government: A weak or ineffective central government may be unable to maintain control over a diverse region, allowing centrifugal forces to take hold.
- External intervention: Foreign powers may support or encourage the fragmentation of a region to weaken it or gain control over its resources.
Consequences of Balkanization
- Political instability: Balkanized regions are often plagued by violence, conflict, and political instability as different groups compete for power and territory.
- Economic underdevelopment: Fragmentation can hinder economic development by disrupting trade and investment and creating barriers to cooperation.
- Humanitarian crises: Conflict and instability can result in human rights violations, displacement of populations, and humanitarian crises.
- International tensions: Balkanization can create tensions between neighboring states, as ethnic groups or political movements cross borders.
Examples of Balkanization
- The Balkan Peninsula: The historical fragmentation of the Balkan Peninsula, with its diverse ethnic and religious groups, is the classic example of Balkanization.
- The former Yugoslavia: The collapse of Yugoslavia in the 1990s led to the creation of several independent states along ethnic lines, resulting in widespread conflict and human suffering.
- The Middle East: The ongoing fragmentation of the Middle East, driven by political and sectarian divides, has created a geopolitical landscape characterized by instability and conflict.
Addressing Balkanization
Addressing the causes and consequences of Balkanization requires a multifaceted approach:
- Promoting national unity: Building a sense of shared identity and belonging among diverse groups is crucial for overcoming divisions and fostering cooperation.
- Resolving historical grievances: Addressing past injustices and conflicts through mechanisms such as truth and reconciliation commissions can help heal wounds and lay the foundation for reconciliation.
- Strengthening central government: A strong and effective central government can provide stability, mediate conflicts, and ensure the equitable distribution of resources.
- Preventing external intervention: Minimizing external interference and supporting peaceful resolution of internal conflicts can help prevent Balkanization from taking hold.
Conclusion
Balkanization is a complex and challenging phenomenon that can have devastating consequences for regions and their people. By understanding its causes and consequences, and by developing proactive strategies to address these issues, we can work towards preventing and mitigating the negative effects of Balkanization.
Useful Tables
| Table 1: Examples of Balkanization in History |
|—|—|
| The Balkan Peninsula | The former Yugoslavia |
| The Middle East | The Soviet Union |
| The Indian subcontinent | Africa |
| Asia | The Americas |
| Table 2: Causes of Balkanization |
|—|—|
| Ethnic and cultural diversity | Historical grievances |
| Weak central government | External intervention |
| Table 3: Consequences of Balkanization |
|—|—|
| Political instability | Economic underdevelopment |
| Human rights violations | Displacement of populations |
| Humanitarian crises | International tensions |
| Table 4: Strategies to Address Balkanization |
|—|—|
| Promoting national unity | Resolving historical grievances |
| Strengthening central government | Preventing external intervention |
FAQs
-
What is the difference between Balkanization and secession?
* Balkanization refers to the fragmentation of a region into multiple smaller states, often through conflict or political instability. Secession, on the other hand, refers to the peaceful withdrawal of a territory from a larger state. -
Can Balkanization be a positive process?
* While Balkanization is often associated with negative consequences, it can sometimes lead to the creation of more stable and prosperous states. For example, the secession of Singapore from Malaysia in 1965 led to the creation of a prosperous and stable city-state. -
How can we prevent Balkanization?
* Preventing Balkanization requires addressing its root causes, such as ethnic and cultural diversity, historical grievances, weak central government, and external intervention. -
What role can international organizations play in addressing Balkanization?
* International organizations can play a crucial role in mediating conflicts, providing humanitarian assistance, and supporting peacebuilding efforts in balkanized regions. -
How can we promote national unity in diverse regions?
* Promoting national unity requires building a sense of shared identity and belonging among diverse groups through education, cultural exchanges, and other initiatives. -
What are the challenges to resolving historical grievances?
* Resolving historical grievances can be challenging, as they often involve deeply rooted emotions and competing narratives. However, it is essential to address these grievances through truth and reconciliation mechanisms to build lasting peace. -
How can we strengthen central governments in balkanized regions?
* Strengthening central governments requires addressing issues such as corruption, weak institutions, and lack of accountability. This can be achieved through democratic reforms, capacity building, and international support. -
Is external intervention always harmful in balkanized regions?
* While external intervention can sometimes escalate conflicts, it can also play a positive role in mediating peace and providing humanitarian assistance. However, it is important for external actors to act impartially and respect the sovereignty of the affected region.