Understanding GPA Calculations
Grade point average (GPA) is a numerical representation of a student’s academic performance, calculated by dividing the total grade points earned by the total number of courses taken. Two common types of GPA calculations exist: weighted and unweighted.

Weighted GPA
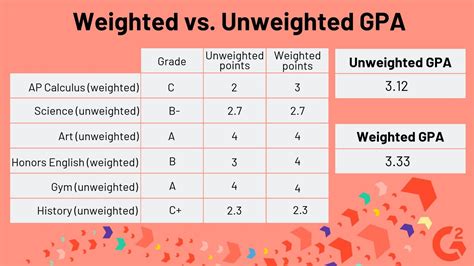
Definition: A weighted GPA considers the difficulty level of courses when calculating the GPA. Courses with higher difficulty levels, such as honors or Advanced Placement (AP) courses, carry a higher weight, resulting in a higher GPA boost for students who earn high grades in those courses.
Purpose: Weighted GPA aims to reward students for taking challenging academic courses, providing a more accurate representation of their abilities and academic rigor.
Unweighted GPA
Definition: An unweighted GPA does not consider course difficulty when calculating the GPA. All courses are treated equally, and each letter grade receives a predetermined numerical value, regardless of the difficulty level of the course.
Purpose: Unweighted GPA provides a straightforward and consistent measure of academic performance, allowing for easier comparisons between students who have taken different courses.
Key Differences
| Feature | Weighted GPA | Unweighted GPA |
|---|---|---|
| Difficulty Level | Considered | Not Considered |
| Grade Boost | Given for challenging courses | Not Given |
| Accuracy | More accurate for assessing academic rigor | Less accurate in this regard |
| Purpose | Reward students for taking challenging courses | Provide a consistent measure of performance |
Pros and Cons
Weighted GPA:
-
Pros:
- Rewards students for academic rigor
- Provides a more accurate reflection of academic abilities
-
Cons:
- Can inflate GPAs for students who take many easy courses
- Creates a competitive environment where students may feel pressured to take only challenging courses
Unweighted GPA:
-
Pros:
- Provides a fair and consistent measure of performance
- Simplifies comparisons between students
-
Cons:
- Does not recognize the difficulty of courses
- May not accurately reflect students’ academic abilities
Which GPA is Better?
The choice between a weighted and unweighted GPA depends on the individual student’s goals and circumstances.
Weighted GPA: Suitable for students who:
* Have taken challenging academic courses
* Want to demonstrate their academic rigor
* Are applying to competitive colleges or universities
Unweighted GPA: Suitable for students who:
* Have taken a mix of challenging and easier courses
* Want a straightforward and consistent measure of performance
* Are not applying to highly selective schools
How to Calculate Weighted and Unweighted GPA
Weighted GPA:
- Assign a weight to each course based on its difficulty level. Common weights include:
- Standard courses: 1.0
- Honors courses: 1.1
- AP/IB courses: 1.2
- Multiply each course grade by its weight.
- Add up the weighted grade points.
- Divide the total weighted grade points by the total number of courses taken.
Unweighted GPA:
- Assign a numerical value to each letter grade (e.g., A = 4.0, B = 3.0).
- Multiply each course grade by its numerical value.
- Add up the total grade points.
- Divide the total grade points by the total number of courses taken.
FAQs
Q1: Can I have both a weighted and unweighted GPA?
A: Yes, many schools provide both a weighted and unweighted GPA on transcripts.
Q2: Which GPA do colleges consider?
A: Most colleges consider both weighted and unweighted GPAs during the admissions process.
Q3: How important is GPA for college admissions?
A: GPA is a significant factor in college admissions, but it is not the only factor considered. Extracurricular activities, essays, and standardized test scores also play a role.
Q4: Can I improve my GPA after high school?
A: Yes, taking college courses or attending summer school can help improve GPA.
Q5: What is a good GPA?
A: A good GPA is typically considered to be above 3.5 for unweighted and above 4.0 for weighted.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between weighted and unweighted GPA is essential for students looking to optimize their academic performance and prepare for college admissions. By choosing the GPA calculation that best aligns with their goals and strengths, students can accurately represent their academic abilities and maximize their chances of success.