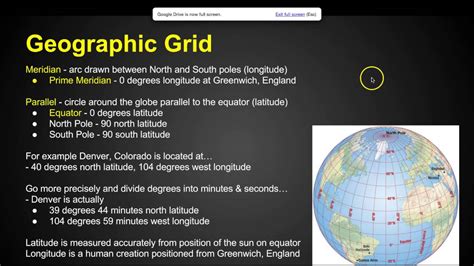
AP Human Geography, a social studies course offered to high school juniors and seniors, is designed to provide students with an understanding of the patterns and processes that shape the human landscape. The course focuses on the relationship between human societies and their physical environment, as well as the cultural, economic, and political forces that drive human activity.

Keywords
- AP Human Geography
- Social studies
- High school
- Human landscape
- Physical environment
- Cultural forces
- Economic forces
- Political forces
Why it Matters
AP Human Geography is a valuable course for students who are interested in pursuing a career in the social sciences, such as geography, sociology, or economics. The course also provides students with a strong foundation in critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are essential for success in college and beyond.
Benefits
- Develop a strong understanding of the patterns and processes that shape the human landscape.
- Learn about the cultural, economic, and political forces that drive human activity.
- Gain critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Prepare for college-level work in the social sciences.
What You Will Learn
In AP Human Geography, you will learn about the following topics:
- The nature of geography and its relationship to other disciplines.
- The physical environment and its influence on human societies.
- The cultural landscape and the diversity of human cultures.
- The economic landscape and the global economy.
- The political landscape and the role of governments.
- The population landscape and the challenges of population growth.
- The urban landscape and the challenges of urbanization.
How to be Successful in AP Human Geography
To be successful in AP Human Geography, you should:
- Attend class regularly and take notes.
- Read the assigned textbook and complete all homework assignments.
- Participate in class discussions and ask questions.
- Study for exams regularly.
- Take advantage of extra help from your teacher.
Resources
The following resources can help you succeed in AP Human Geography:
- The College Board’s AP Human Geography website
- The Khan Academy’s AP Human Geography course
- The Crash Course AP Human Geography series
FAQs
1. What is the format of the AP Human Geography exam?
The AP Human Geography exam is a three-hour exam that consists of two sections: a multiple-choice section and a free-response section.
2. How is the AP Human Geography exam scored?
The multiple-choice section is scored on a scale of 0 to 5 points. The free-response section is scored on a scale of 0 to 9 points. The total score for the exam is a weighted average of the multiple-choice and free-response scores.
3. What is a good score on the AP Human Geography exam?
A score of 3 or higher on the AP Human Geography exam is considered a passing score. A score of 4 or 5 on the exam is considered a good score.
4. How can I prepare for the AP Human Geography exam?
The best way to prepare for the AP Human Geography exam is to take a course in the subject. You can also study for the exam using the resources listed above.
5. What are the benefits of taking AP Human Geography?
Taking AP Human Geography can help you develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills, gain a strong understanding of the human landscape, and prepare for college-level work in the social sciences.
6. What are some careers that I can pursue with a degree in human geography?
With a degree in human geography, you can pursue a variety of careers, such as:
- Geographer
- Urban planner
- Environmental consultant
- GIS analyst
- Market researcher
Table 1: Key Concepts in AP Human Geography
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Culture | The shared beliefs, values, and practices of a group of people. |
| Economics | The study of how societies produce, distribute, and consume goods and services. |
| Geography | The study of the Earth’s surface and its human and environmental interactions. |
| History | The study of past events and their impact on the present. |
| Politics | The study of power and its distribution in society. |
| Religion | The belief in and worship of a superhuman power or powers. |
| Sociology | The study of human societies and their interactions. |
Table 2: The Five Themes of Geography
| Theme | Definition |
|---|---|
| Location | The position of a place on Earth’s surface. |
| Place | The unique characteristics of a place. |
| Interaction | The relationship between people and their environment. |
| Movement | The movement of people, goods, and ideas. |
| Region | An area with similar characteristics. |
Table 3: The Seven Continents
| Continent | Area (sq km) | Population (2020) |
|---|---|---|
| Asia | 44,614,000 | 4.6 billion |
| Africa | 30,365,000 | 1.3 billion |
| North America | 24,230,000 | 360 million |
| South America | 17,840,000 | 430 million |
| Antarctica | 14,200,000 | 0 |
| Europe | 10,180,000 | 740 million |
| Australia | 8,525,989 | 26 million |
Table 4: The World’s Largest Cities
| Rank | City | Country | Population (2020) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tokyo | Japan | 37,339,804 |
| 2 | Delhi | India | 28,514,000 |
| 3 | Shanghai | China | 26,319,000 |
| 4 | São Paulo | Brazil | 21,650,000 |
| 5 | Mexico City | Mexico | 21,581,000 |
| 6 | Cairo | Egypt | 20,418,000 |
| 7 | Beijing | China | 21,542,000 |
| 8 | Mumbai | India | 20,974,000 |
| 9 | Osaka | Japan | 19,281,000 |
| 10 | New York City | United States | 20,140,000 |