An applied math degree provides you with a versatile foundation in mathematics and its applications, opening doors to a wide range of careers in various industries.

Data Science and Analytics
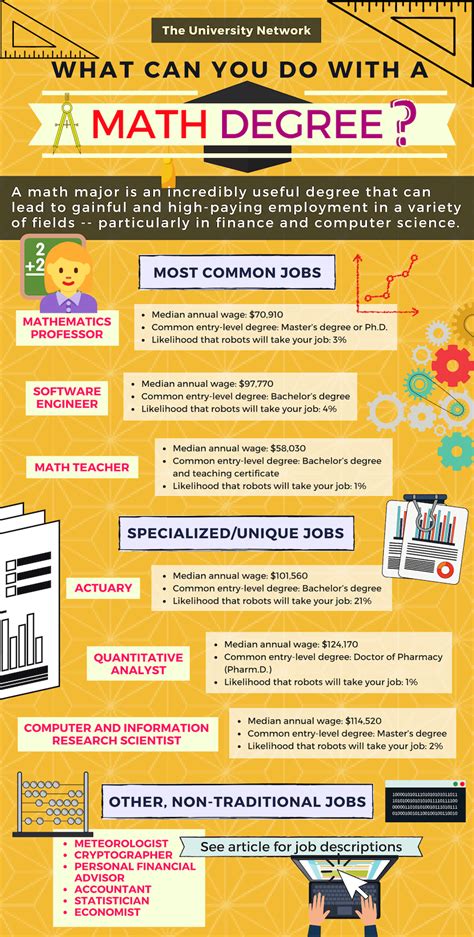
- Data Scientist: Analyze and interpret large datasets, using statistical modeling and machine learning to extract insights and support decision-making. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual salary for data scientists is $126,830 as of May 2021.
- Data Analyst: Collect, clean, and prepare data, identifying trends and patterns to improve business operations. The BLS reports a median salary of $65,210 for data analysts as of May 2021.
Finance and Risk Management
- Quantitative Analyst (Quant): Develop and implement mathematical models to evaluate financial instruments, assess risks, and make investment decisions. The average annual salary for quants in the United States is $120,000, according to Salary.com.
- Risk Analyst: Analyze and mitigate risks within financial institutions, ensuring regulatory compliance and minimizing potential losses. As of May 2021, the BLS reports a median salary of $101,220 for risk analysts.
Engineering and Technology
- Software Engineer: Design, develop, and maintain software applications, using mathematical algorithms and data structures to solve complex problems. The median annual salary for software engineers is $110,140 as of May 2021, according to the BLS.
- Computational Scientist: Apply mathematical models and simulations to solve scientific and engineering problems, such as weather forecasting, drug discovery, and materials science. The median salary for computational scientists is $117,900 as of May 2021.
Other Industries
- Actuary: Use mathematical and statistical techniques to assess and manage financial risks in areas such as insurance, pensions, and investments. According to the Society of Actuaries, the median annual salary for actuaries is $108,370 as of 2020.
- Operations Research Analyst: Optimize operations and improve decision-making in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare using mathematical models and techniques. The BLS reports a median salary of $85,280 for operations research analysts as of May 2021.
- Strong foundation in mathematics, including calculus, linear algebra, differential equations, and statistics
- Proficiency in programming languages such as Python, R, and MATLAB
- Expertise in data analysis and machine learning techniques
- Ability to communicate and interpret mathematical results effectively
- Problem-solving and critical thinking skills
- Strong attention to detail and accuracy
- Gain practical experience through internships and projects: Apply your mathematical skills to real-world problems and gain valuable insights.
- Develop your soft skills: Enhance your communication, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities to succeed in a collaborative work environment.
- Stay updated on the latest technologies and trends: Continuously learn and explore new areas of applied mathematics to remain competitive.
- Network with professionals: Attend conferences, join online forums, and connect with individuals in your field to expand your knowledge and career opportunities.
Pros:
- High earning potential in various industries
- Versatile skill set applicable to multiple fields
- Strong foundation for future graduate studies in mathematics or related fields
Cons:
- Can be challenging to find entry-level positions in certain industries
- Requires a strong commitment to continuous learning and development
- May require relocation for specific career opportunities
1. What is the job outlook for applied mathematicians?
According to the BLS, the job outlook for mathematical scientists, including applied mathematicians, is expected to grow 33% from 2020 to 2030, much faster than the average for all occupations.
2. Can I pursue an applied math degree with a non-STEM background?
While a strong background in mathematics, science, and technology is preferred, it is possible to pursue an applied math degree with a non-STEM background if you have a strong foundation in mathematics and are willing to work hard.
3. What industries hire applied mathematicians?
Applied mathematicians are in demand in a wide range of industries, including finance, technology, engineering, manufacturing, healthcare, and government.
4. What is the difference between applied mathematics and pure mathematics?
Applied mathematics focuses on the application of mathematical principles to solve real-world problems, while pure mathematics involves the study of mathematical concepts and theories for their own sake.
5. What is a creative new word to generate ideas for new applications of applied mathematics?
“Mathavation”: A combination of mathematics and innovation, used to spark creative thinking and explore new possibilities for applying mathematical concepts.
6. What are some useful tables for applied mathematicians?
| Table | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Trigonometric Functions | Values of sine, cosine, and tangent | sin(30°) = 1/2 |
| Laplace Transforms | Transforms functions from the time domain to the frequency domain | Laplace{e^(-t)} = 1/(s+1) |
| Integration Techniques | Methods for finding integrals | Integral of sin(x) dx = -cos(x) |
| Probability Distributions | Statistical distributions used to model random variables | Normal distribution, Poisson distribution |
7. Can I work as a data scientist with an applied math degree?
Yes, an applied math degree provides a strong foundation for a career as a data scientist. Data science combines elements of mathematics, statistics, and computer science to extract insights from data.