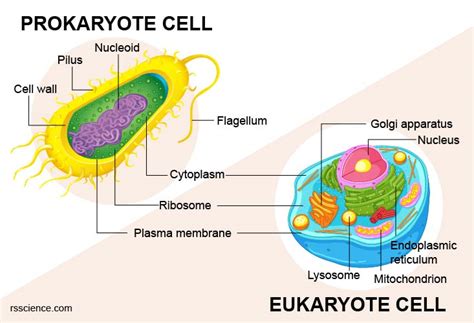
Cells are the fundamental unit of life, and they come in two basic types: eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Eukaryotes are more complex than prokaryotes, and they have a number of organelles that prokaryotes do not. However, there are also a few organelles that are common to both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.

4 Organelles Found in Both Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
The four organelles that are found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes are:
- Ribosomes
- Plasma membrane
- Cytoplasm
- DNA
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis. They are made up of RNA and protein, and they are found in all cells. Ribosomes are essential for cell growth and function, and they play a key role in the production of proteins that are needed for a variety of cellular processes.
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is a thin layer of lipids that surrounds the cell. It acts as a barrier between the cell and its surroundings, and it regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell. The plasma membrane is also responsible for maintaining the cell’s shape and for providing a stable environment for the cell’s internal components.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell. It contains all of the cell’s organelles, and it is where most of the cell’s metabolic activities take place. The cytoplasm is also responsible for transporting materials within the cell.
DNA
DNA is the genetic material of the cell. It contains the instructions for all of the cell’s activities, and it is responsible for transmitting genetic information from one generation to the next. DNA is found in the nucleus of eukaryotes, and it is found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes.
Conclusion
The four organelles that are found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes are essential for cell growth and function. They play a key role in a variety of cellular processes, and they are essential for the survival of all cells.