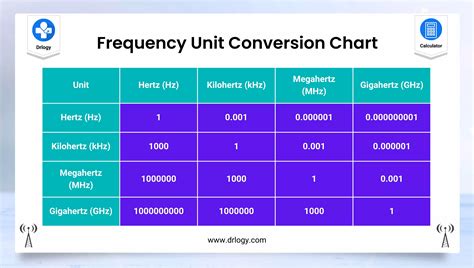
With the rapid advancements in technology, particularly in the digital realm, understanding the conversion between different frequency units has become increasingly important. Whether you’re dealing with audio signals, electromagnetic waves, or any other periodic phenomena, converting between w (radians per second) and Hz (Hertz) is crucial for accurate measurements and analysis. This comprehensive guide will provide you with all the necessary information, formulas, and practical applications to confidently navigate the world of frequency conversion from w to Hz.

Understanding the Concepts
Radians per Second (w)
Radians per second (w) is a unit of angular velocity that measures the rate of change of angular displacement. It is defined as the angular displacement (in radians) divided by the time (in seconds) taken to complete that displacement. In other words, it measures how quickly an object is rotating or oscillating.
Hertz (Hz)
Hertz (Hz) is the SI unit of frequency that measures the number of occurrences of a periodic event per second. It is often used to describe the frequency of sound waves, electromagnetic waves, and other periodic signals. In the context of w to Hz conversion, Hz represents the number of complete cycles (or oscillations) that occur within one second.
The Formula for Converting w to Hz
Converting w (radians per second) to Hz (Hertz) is straightforward using the following formula:
f = w / 2π
where:
- f is the frequency in Hz
- w is the angular velocity in radians per second
Applications of w to Hz Conversion
The conversion between w and Hz has numerous practical applications across various fields, including:
- Audio Engineering: Converting between w and Hz is essential for designing and analyzing audio filters, synthesizers, and sound effects.
- Electromagnetism: Hz to w conversion is used to calculate the frequency of electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves, microwaves, and infrared radiation.
- Physics: Oscillations and vibrations in mechanical systems can be described in terms of w and Hz, enabling the study of resonance and energy transfer.
- Data Acquisition: Converting sensor data from w to Hz can help extract meaningful information about periodic events, such as heart rate monitors and motion detectors.
Tips and Tricks
- Memorize the Conversion Factor: The conversion factor 2π is a common value that should be memorized to simplify the calculation mentally.
- Use a Conversion Calculator: Numerous online and offline tools can instantly perform w to Hz conversions, saving time and effort.
- Pay Attention to Units: Ensure that the input and output units are consistent to avoid errors.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing Angular Velocity and Frequency: Angular velocity (w) and frequency (f) are related but distinct concepts. Do not interchange them during conversion.
- Using Incorrect Conversion Factor: The conversion factor 2π is crucial; using any other value will result in incorrect calculations.
- Ignoring Unit Conversion: Always convert between the appropriate units (radians per second and Hertz) before performing the calculation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
How do I convert 100 Hz to w?
– w = 2πf = 2π * 100 Hz = 200π radians per second -
What is the angular velocity of a sound wave with a frequency of 440 Hz?
– w = 2πf = 2π * 440 Hz = 880π radians per second -
Can I convert w to Hz for non-periodic signals?
– No, the w to Hz conversion is only applicable to periodic signals that have a well-defined frequency. -
What is the relationship between w and angular frequency?
– Angular frequency (ω) is equivalent to w, and they are often used interchangeably. -
How is w to Hz conversion used in data acquisition?
– Converting sensor data from w to Hz allows for the identification and analysis of periodic patterns and events in the data. -
What is a potential application of w to Hz conversion in the medical field?
– Converting electrocardiogram (ECG) data from w to Hz can reveal important information about heart rate and rhythm disorders. -
Can I use the w to Hz formula for converting angular displacement to time?
– No, the w to Hz formula is not suitable for converting angular displacement to time. It is specifically designed for converting angular velocity to frequency. -
What is the difference between radians per minute (rpm) and Hz?
– While both rpm and Hz measure frequency, they represent different rates. 1 Hz is equivalent to 60 rpm.