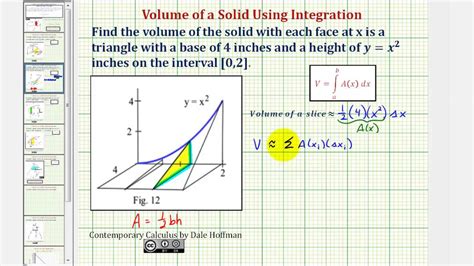
The volume of cross section, a fundamental concept in geometry, plays a crucial role in various fields, from architecture and engineering to biology and medicine. It provides invaluable insights into the size, shape, and composition of objects and spaces, enabling us to understand their properties and functions more effectively.

## Understanding Volume of Cross Section
The volume of cross section is defined as the area of the section of an object cut by a plane. This area represents the amount of space occupied by the object in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the section. By cutting an object at different planes, we can obtain multiple cross sections, each providing a unique perspective on the object’s internal structure.
In the case of a rectangular prism, a cross section parallel to the base will yield a rectangle, while a cross section perpendicular to the base will produce a square. These cross sections reveal information about the prism’s length, width, and height. Similarly, cross sections of complex shapes, such as cylinders, cones, and spheres, provide insights into their radii, heights, and volumes.
## Importance of Volume of Cross Section
The volume of cross section holds tremendous importance in numerous applications:
## Architecture and Engineering
- Determining the weight-bearing capacity of structures by calculating the cross-sectional area of beams, columns, and other load-bearing elements.
- Designing bridges, tunnels, and other infrastructure projects by evaluating the volume of soil or rock that needs to be excavated or filled.
- Optimizing the placement of windows and doors in buildings to ensure proper ventilation and natural lighting.
## Biology and Medicine
- Analyzing the size, shape, and density of biological specimens, such as cells, tissues, and organs, using cross-sectional images obtained from microscopy or medical imaging techniques.
- Detecting abnormalities or diseases by comparing the volume of cross sections to reference values.
- Developing treatments and surgical procedures by understanding the internal structure and volume of organs and tissues.
## Applications in Various Fields
The concept of volume of cross section extends beyond traditional disciplines, opening up new avenues for innovation and discovery:
## Geography and Earth Sciences
- Estimating the volume of water flow in rivers and streams by measuring the cross-sectional area of their channels.
- Determining the volume of soil erosion or deposition in watersheds by analyzing cross sections of terrain.
- Mapping the distribution of subsurface geological features by interpreting cross sections of seismic or electrical resistivity data.
## Manufacturing and Industry
- Optimizing the cutting and shaping of materials by calculating the cross-sectional area of raw stock.
- Determining the volume of materials in storage tanks or silos for inventory control and management.
- Designing molds and dies for casting or forming processes based on the cross-sectional shape of the desired product.
## Table 1: Volume of Cross Sections of Regular Shapes
| Shape | Cross Section | Volume of Cross Section |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | Rectangle | Area of rectangle = length x width |
| Circle | Circle | Area of circle = πr2 |
| Triangle | Triangle | Area of triangle = (1/2) * base * height |
| Sphere | Circle | Area of circle = πr2 |
| Cone | Circle | Area of circle = πr2 |
| Cylinder | Circle | Area of circle = πr2 |
## Table 2: Applications of Volume of Cross Section in Biology
| Application | Cross Section | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Cell biology | Microscopy images | Determining cell size, shape, and volume |
| Tissue engineering | MRI scans | Designing scaffolds for tissue growth and regeneration |
| Organ transplantation | CT scans | Evaluating organ size and compatibility before transplant |
| Cancer diagnosis | PET scans | Detecting and staging cancerous tumors |
| Drug delivery | Microtomography | Optimizing drug delivery systems by studying the volume of capillary beds |
## Table 3: Examples of Cross-Sectional Analysis in Engineering
| Project | Cross Section | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Bridge design | Cross section of bridge deck | Determining the weight-bearing capacity and structural integrity of the bridge |
| Tunnel construction | Cross section of tunnel bore | Estimating the volume of material to be excavated and the dimensions of the tunnel lining |
| Building renovation | Cross section of building frame | Evaluating the load-bearing capacity of columns and beams and identifying potential structural weaknesses |
| Wind turbine design | Cross section of wind turbine blade | Optimizing the shape and volume of blades to maximize energy efficiency |
| Aerospace engineering | Cross section of aircraft wing | Analyzing the aerodynamic forces acting on the aircraft and designing wings for optimal performance |
## Table 4: Emerging Applications of Volume of Cross Section
| Field | Application | Cross Section |
|---|---|---|
| Marine engineering | Underwater vehicle design | Cross section of vehicle hull |
| Robotics | Surgical robot design | Cross section of robotic arms and instruments |
| Archaeology | Analysis of ancient artifacts | Cross section of artifacts |
| Forensics | Analysis of crime scenes | Cross section of evidence, such as bullet trajectories and blood spatter |
| Urban planning | Smart city design | Cross section of urban infrastructure, such as roads and buildings |