Introduction
The Virginia Plan, proposed at the 1787 Constitutional Convention, played a pivotal role in shaping the framework of the United States government. As a key component of the convention’s proceedings, the plan introduced bold ideas that aimed to strengthen the central government and create a more effective union among the states.

Key Provisions of the Virginia Plan
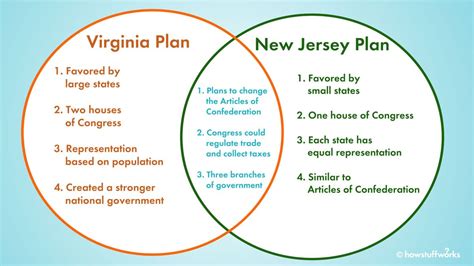
- Strong Central Government: The plan called for a three-branch federal government with a strong executive, legislative, and judicial structure.
- Bicameral Legislature: It proposed a two-chamber legislature, with the House of Representatives based on population and the Senate representing equal state interests.
- Supreme Court: The plan established a Supreme Court as the highest court in the land, with authority to interpret the Constitution and overrule unconstitutional laws.
- Chief Executive: The plan created the office of President, who would serve as the head of state and commander-in-chief.
The Great Compromise
One of the most significant debates during the Constitutional Convention revolved around the issue of representation in the legislature. Smaller states feared being dominated by larger states, while larger states demanded representation based on population. The Great Compromise, a proposal put forth by Connecticut, resolved this conflict by establishing the bicameral legislature described in the Virginia Plan.
Impact on the United States Constitution
The Virginia Plan served as the foundation for the United States Constitution. Many of its provisions, including the three-branch government, bicameral legislature, and Supreme Court, were incorporated into the final document. The plan significantly strengthened the central government and created a more unified and stable nation.
Historical Context
The Virginia Plan was a product of the post-Revolutionary War period, during which the United States faced challenges in governing under the weak Articles of Confederation. The plan reflected the prevailing desire for a stronger central authority to promote economic growth, protect national security, and maintain order.
Impact on Contemporary Political Thought
The Virginia Plan continues to influence political thought today. Its principles of federalism, separation of powers, and checks and balances form the basis of democratic governments worldwide. The plan’s emphasis on the rule of law and the protection of individual rights remains a guiding force in contemporary political discourse.
Common Criticisms of the Virginia Plan
Despite its historical significance, the Virginia Plan has also faced criticism over the years:
- Lack of Direct Democracy: The plan limited the role of direct democracy in government, which some critics argue diminishes citizen participation.
- Representation Imbalance: The bicameral legislature’s structure potentially gives greater power to smaller states, potentially undermining the principle of equal representation.
- Skewed Electoral College: The plan established the Electoral College system for electing the President, which some argue has led to instances of a candidate winning the popular vote but losing the presidency.
Modern Applications of the Virginia Plan
The principles enshrined in the Virginia Plan continue to find relevance in modern applications:
- Corporate Governance: The plan’s separation of powers and checks and balances can be applied in corporate governance to prevent the concentration of excessive power in the hands of any one individual or group.
- Educational Reform: The plan’s emphasis on a republican form of government requires an educated citizenry. Modern educational reforms can emphasize civics and political science to foster civic engagement and strengthen democratic institutions.
- Technology Regulation: The plan’s provisions on interstate commerce and the protection of intellectual property can guide policymakers in regulating emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and the internet of things.
Conclusion
The Virginia Plan, a bold and transformative blueprint for the United States government, remains a testament to the vision and ingenuity of the Founding Fathers. Its principles of federalism, separation of powers, and the rule of law have shaped the American political system and continue to inspire nations around the globe in the quest for a more just and equitable society.
Table 1: Key Provisions of the Virginia Plan
| Provision | Description |
|---|---|
| Strong Central Government | Three-branch government with executive, legislative, and judicial branches |
| Bicameral Legislature | House of Representatives (population-based) and Senate (equal state representation) |
| Supreme Court | Highest court in the land, with authority to interpret the Constitution |
| Chief Executive | President as head of state and commander-in-chief |
Table 2: The Great Compromise
| Plan | Representation |
|---|---|
| New Jersey Plan | Unicameral legislature, equal representation for all states |
| Virginia Plan | Bicameral legislature, population-based representation in the House, equal state representation in the Senate |
| Great Compromise | Bicameral legislature, with population-based representation in the House and equal state representation in the Senate |
Table 3: Impact on the United States Constitution
| Virginia Plan Provision | U.S. Constitution Provision |
|---|---|
| Strong Central Government | Article I, Section 1 |
| Bicameral Legislature | Article I, Sections 2-7 |
| Supreme Court | Article III, Section 1 |
| Chief Executive | Article II, Section 1 |
Table 4: Common Criticisms of the Virginia Plan
| Criticism | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Lack of Direct Democracy | Limits citizen participation in government |
| Representation Imbalance | Potentially gives greater power to smaller states |
| Skewed Electoral College | Can result in a candidate winning the popular vote but losing the presidency |
FAQs
-
What was the main purpose of the Virginia Plan?
– To strengthen the central government and create a more effective union among the states. -
Who proposed the Virginia Plan?
– James Madison, Edmund Randolph, and George Wythe. -
What was the most controversial aspect of the Virginia Plan?
– The issue of representation in the legislature. -
How was the conflict over representation resolved?
– Through the Great Compromise, which established a bicameral legislature with population-based representation in the House and equal state representation in the Senate. -
What is the legacy of the Virginia Plan?
– It laid the foundation for the United States Constitution and has influenced political thought and governance worldwide. -
Does the Virginia Plan still have relevance today?
– Yes, its principles of federalism, separation of powers, and the rule of law continue to guide modern political systems. -
What are some modern applications of the Virginia Plan?
– Corporate governance, educational reform, and technology regulation. -
What are some criticisms of the Virginia Plan?
– Lack of direct democracy, representation imbalance, and skewed Electoral College.