Delving into the Chemistry of Lead Nitrate
Lead nitrate, also known as plumbous nitrate, is a fascinating inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb(NO3)2. This crystalline substance plays a significant role in various industrial and scientific applications, and understanding its molar mass is crucial for accurate stoichiometric calculations and exploring its potential.

Molar Mass: Unveiling the Compound’s Mass
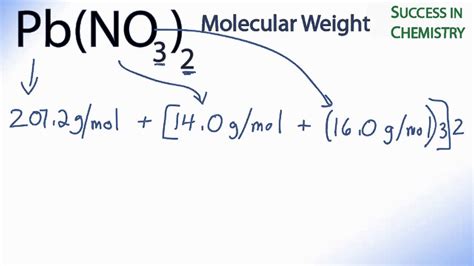
The molar mass of a compound represents the total mass of one mole of that substance. For Pb(NO3)2, the molar mass is calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent elements:
Pb: 207.2 g/mol
N: 14.01 g/mol
O: 32.00 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of Pb(NO3)2 is:
Pb(NO3)2 = 207.2 g/mol + 2(14.01 g/mol) + 2(32.00 g/mol)
= 331.22 g/mol
Understanding the molar mass of Pb(NO3)2 allows chemists to precisely determine the amount of the compound required in various reactions and applications.
Applications: Unlocking the Potential of Lead Nitrate
Pb(NO3)2 finds diverse applications across various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Pb(NO3)2 is utilized in the production of lead-based pigments, such as lead oxide, which are used in paints, ceramics, and glass.
- Photography: It serves as a component in photographic chemicals, contributing to the development of photographic images.
- Textile Industry: Pb(NO3)2 is employed as a mordant in textile dyeing, enhancing the adhesion of dyes to fabrics.
- Pyrotechnics: It’s a key ingredient in fireworks, contributing to their characteristic colors and sound effects.
Benefits: Exploring the Advantages of Pb(NO3)2
The use of Pb(NO3)2 brings forth several advantages:
- Stability: Pb(NO3)2 exhibits remarkable stability under ambient conditions, making it a reliable compound for various applications.
- Solubility: It readily dissolves in water, facilitating its use in aqueous solutions.
- Versatility: Its diverse applications in different industries showcase its versatility and practical utility.
Comparative Analysis: Lead Nitrate vs. Alternative Compounds
When considering the use of Pb(NO3)2, it’s essential to compare its properties with alternative compounds to make informed decisions.
| Property | Pb(NO3)2 | Alternative Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Molar Mass | 331.22 g/mol | PbCl2: 278.10 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in water | PbSO4: Insoluble in water |
| Toxicity | Toxic | Ca(NO3)2: Relatively non-toxic |
This comparative analysis highlights the unique characteristics of Pb(NO3)2, enabling users to select the most suitable compound for their specific applications.
Health and Environmental Considerations
Pb(NO3)2 is a toxic substance, and its handling requires appropriate safety precautions. Exposure to lead compounds, including Pb(NO3)2, can lead to various health concerns, such as:
- Neurodevelopmental disorders
- Kidney damage
- Reproductive issues
It’s crucial to adhere to safety regulations, wear protective gear when handling Pb(NO3)2, and ensure proper disposal methods to minimize environmental contamination.
Innovations: Expanding the Applications of Pb(NO3)2
Researchers are constantly exploring innovative ways to harness the properties of Pb(NO3)2. One such approach has led to the development of a novel material known as “plumbionic”.
Plumbionic combines Pb(NO3)2 with other materials to create composites with enhanced properties. These composites have applications in:
- Energy storage
- Biomedical devices
- Optical coatings
Plumbionic leverages the unique properties of Pb(NO3)2, opening up exciting possibilities for future advancements.
Tables: Comprehensive Data for Pb(NO3)2
Table 1: Physical Properties of Pb(NO3)2
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 4.53 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 470°C |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes at 200°C |
Table 2: Solubility of Pb(NO3)2 in Various Solvents
| Solvent | Solubility (g/100 mL) |
|---|---|
| Water | 53.1 |
| Ethanol | 0.24 |
| Acetone | Insoluble |
Table 3: Applications of Pb(NO3)2 in Different Industries
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Lead-based pigments, glass production |
| Photography | Photographic chemicals |
| Textile Industry | Mordant in dyeing |
| Pyrotechnics | Fireworks |
Table 4: Environmental and Health Considerations
| Concern | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | Handle with caution, wear protective gear |
| Environmental Impact | Dispose of properly to minimize contamination |
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the molecular weight of Pb(NO3)2?
– The molecular weight of Pb(NO3)2 is 331.22 g/mol. -
Is Pb(NO3)2 soluble in water?
– Yes, Pb(NO3)2 is soluble in water, with a solubility of 53.1 g/100 mL at room temperature. -
What are the applications of Pb(NO3)2 in photography?
– Pb(NO3)2 is used in photographic chemicals to contribute to image development. -
Is Pb(NO3)2 toxic?
– Yes, Pb(NO3)2 is a toxic substance, and proper safety precautions should be taken when handling it. -
How is Pb(NO3)2 disposed of safely?
– Pb(NO3)2 should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations to minimize environmental contamination. -
What is the role of Pb(NO3)2 in the production of lead-based pigments?
– Pb(NO3)2 is used as a starting material in the production of lead-based pigments, such as lead oxide, which are used in paints, ceramics, and glass. -
How does Pb(NO3)2 contribute to the colors in fireworks?
– Pb(NO3)2 is used in fireworks to produce characteristic colors, particularly yellow and green. -
What is plumbionic, and how is it related to Pb(NO3)2?
– Plumbionic