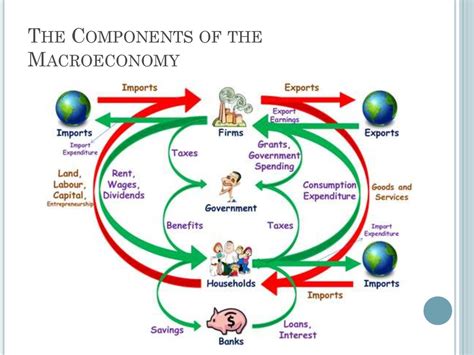
Introduction
Macroeconomics is a broad field that studies the economy as a whole, focusing on topics such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. To understand macroeconomics effectively, it’s essential to master its key units, each covering a specific aspect of economic behavior. This article provides a comprehensive overview of macroeconomics units, offering a thorough understanding for students, researchers, and practitioners alike.

Unit 1: National Income and Output
This unit introduces the fundamental concepts of national income and output. It covers measures of economic activity such as gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), and net national product (NNP), highlighting their significance in assessing economic performance.
- Key Concepts: GDP, GNP, NNP, GDP components
- Example: The U.S. GDP in 2022 was estimated at $26.49 trillion, reflecting the total value of all goods and services produced in the country during that year.
Unit 2: Inflation and Unemployment
Inflation refers to the persistent increase in the general price level, while unemployment measures the proportion of the labor force that is actively seeking but unable to find work. This unit examines the causes and consequences of both inflation and unemployment, as well as government policies to mitigate their effects.
- Key Concepts: Inflation rate, unemployment rate, Phillips curve
- Example: The annual inflation rate in the Eurozone reached a record high of 10.7% in October 2022, driven primarily by rising energy and food prices.
Unit 3: Money and Banking
This unit explores the role of money in the economy and the banking system’s functions in creating and distributing money. It covers the concepts of fractional reserve banking, the money multiplier, and monetary policy, which are crucial for understanding how central banks influence the economy.
- Key Concepts: Money supply, demand for money, monetary policy instruments
- Example: In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Federal Reserve increased the money supply by purchasing government bonds and other assets, leading to historically low interest rates.
Unit 4: Economic Growth and Development
Economic growth refers to the sustained increase in an economy’s productive capacity, while economic development encompasses broader improvements in living standards, including education, health, and technology. This unit analyzes the factors driving economic growth and the challenges faced by developing countries in achieving sustainable development.
- Key Concepts: Production function, Solow growth model, human capital
- Example: China has experienced rapid economic growth over the past few decades, driven by factors such as massive investment in infrastructure and a skilled labor force.
Unit 5: Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy refers to the government’s use of taxation and spending to influence the economy. This unit examines the various fiscal policy tools, their impact on aggregate demand, and the complexities of budget deficits and national debt.
- Key Concepts: Government spending, taxation, budget deficit, crowding out
- Example: During the 2008 financial crisis, governments around the world implemented expansionary fiscal policies, increasing spending and reducing taxes to stimulate economic activity.
Unit 6: International Economics
This unit explores international trade, finance, and exchange rates, highlighting their impact on domestic economies. It covers concepts such as comparative advantage, the balance of payments, and the role of international financial institutions like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund.
- Key Concepts: Comparative advantage, exchange rate, balance of trade
- Example: The United States is one of the world’s largest importers of goods, with a trade deficit of $877.9 billion in 2021.
Unit 7: Current Economic Issues
This unit addresses contemporary economic issues and challenges, such as the global financial crisis, COVID-19 pandemic, and climate change. It analyzes the macroeconomic implications of these events and explores policy responses to mitigate their effects.
- Key Concepts: Financial crisis, climate change mitigation, economic recovery
- Example: The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on economies worldwide, leading to job losses, business closures, and heightened uncertainty.
Unit 8: Economic Forecasting
Economic forecasting plays a crucial role in business planning, investment decisions, and government policymaking. This unit provides an overview of forecasting methods, from simple time series analysis to complex econometric models, and discusses the challenges and limitations of economic forecasting.
- Key Concepts: Time series analysis, econometric models, economic projections
- Example: The International Monetary Fund forecasts that the global economy will grow by 2.9% in 2023, down from 3.4% in 2022.
Conclusion
Mastering the units of macroeconomics is essential for understanding the complexities of the economy and its impact on individuals, businesses, and nations. By gaining a solid foundation in these units, students, researchers, and practitioners can make informed decisions and navigate the ever-changing macroeconomic landscape effectively.