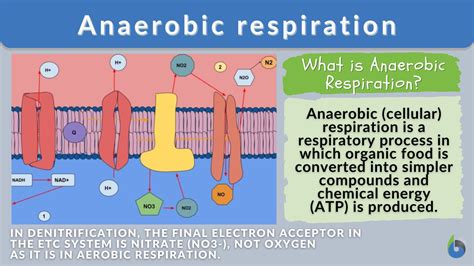
Pyruvate is a key intermediate in the metabolism of glucose, the body’s main energy source. Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle and is ultimately oxidized to produce CO2 and water. However, under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to lactate in a process known as lactate fermentation.

Lactate fermentation is a way for the body to continue to produce energy in the absence of oxygen. It is used by many different types of cells, including muscle cells, red blood cells, and certain types of bacteria. The overall reaction of lactate fermentation is:
Pyruvate + NADH + H+ -> Lactate + NAD+
This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). LDH is found in the cytoplasm of cells and is activated by high levels of NADH. When the concentration of NADH is high, LDH converts pyruvate to lactate in order to regenerate NAD+. This allows the cell to continue to produce energy through glycolysis, even in the absence of oxygen.
Lactate fermentation is a relatively inefficient way to produce energy, as it only yields two molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose. However, it is a valuable way for the body to continue to produce energy in the absence of oxygen.
Lactate fermentation plays an important role in exercise. When muscles are working hard, they need a lot of energy. However, muscles cannot store very much oxygen, so they must rely on anaerobic metabolism to produce energy during intense exercise.
During anaerobic metabolism, lactate fermentation is used to convert pyruvate to lactate. This allows the muscles to continue to produce energy, even in the absence of oxygen. However, lactate fermentation also produces lactic acid, which can cause muscle fatigue.
The amount of lactic acid that is produced during exercise depends on the intensity and duration of the exercise. Low-intensity exercise produces relatively little lactic acid, while high-intensity exercise produces a lot of lactic acid.
Lactate fermentation has several benefits, including:
- It allows the body to continue to produce energy in the absence of oxygen.
- It helps to reduce muscle fatigue.
- It can improve athletic performance.
Lactate fermentation can also have some risks, including:
- It can cause muscle soreness.
- It can lead to dehydration.
- It can increase the risk of heat stroke.
The risks of lactate fermentation can be avoided by:
- Warming up before exercise.
- Cooling down after exercise.
- Staying hydrated.
- Eating a healthy diet.
Lactate fermentation is a valuable way for the body to produce energy in the absence of oxygen. It plays an important role in exercise and can help to improve athletic performance. However, it is important to be aware of the risks of lactate fermentation and to take steps to avoid them.