The molecules of life, DNA and RNA, reside in virtually every cell of every organism on Earth. These molecules hold the instructions for building and maintaining an organism, and they are passed down from parents to offspring.

DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a double-stranded molecule that forms a twisted ladder shape. Each strand of DNA is composed of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The sequence of these nucleotides along the DNA strand determines the genetic code of an organism. The genetic code is essential for DNA to carry out its functions, such as:
- Direct protein synthesis
- Control growth and development
- Guide reproduction and inheritance
- Modify organisms through evolution
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a single-stranded molecule that plays a vital role in protein synthesis and other cellular functions. It is similar to DNA in structure, but it has a different composition. RNA is composed of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
DNA and RNA are essential for life. Without these molecules, cells would not be able to function properly, and organisms would not be able to survive.
DNA is composed of two long chains of nucleotides, which are linked together by hydrogen bonds. The two strands of DNA are twisted around each other to form a double helix. The double helix is stabilized by covalent bonds between the nucleotides on opposite strands. The structure of DNA was discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953.
The genetic code is the sequence of nucleotides in DNA that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins. Proteins are essential for the structure and function of cells. The genetic code is universal, meaning that the same genetic code is used by all organisms on Earth. This means that a gene from a human can be inserted into a bacterium and the bacterium will be able to produce the human protein.
DNA replication is the process by which DNA is copied. Replication occurs before cell division, so that each new cell receives a complete copy of the DNA. The process of DNA replication is very accurate, but errors can occur. These errors can lead to mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral.
DNA is constantly damaged by environmental factors, such as radiation and chemicals. To protect against this damage, cells have a number of DNA repair mechanisms. These mechanisms can repair most types of DNA damage, but they cannot repair all damage. If the damage is too severe, the cell may die.
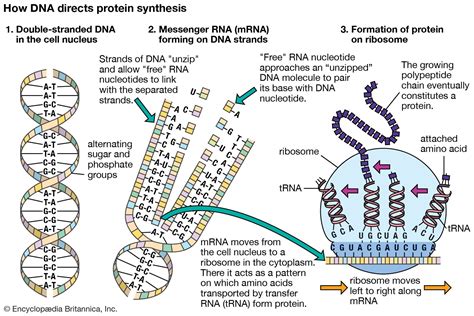
RNA transcription is the process by which RNA is copied from DNA. Transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell. The RNA molecule is then transported to the cytoplasm, where it is used in protein synthesis.
Protein synthesis is the process by which proteins are made. Protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. The ribosome is the molecule that assembles proteins. The ribosome reads the RNA molecule and uses the genetic code to determine the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
DNA and RNA are essential for life, and they have a wide range of applications in medicine, agriculture, and industry.
Medicine
DNA and RNA are used in a variety of medical applications, including:
- Diagnosis of genetic diseases
- Development of new drugs and therapies
- Gene therapy
- Forensic science
Agriculture
DNA and RNA are used in a variety of agricultural applications, including:
- Crop improvement
- Livestock breeding
- Pest control
Industry
DNA and RNA are used in a variety of industrial applications, including:
- Production of biofuels
- Development of new materials
- Environmental cleanup
The field of DNA and RNA research is constantly evolving. New discoveries are being made all the time, and these discoveries are leading to new applications of DNA and RNA in medicine, agriculture, and industry. The future of DNA and RNA is bright, and these molecules will continue to play a vital role in our lives.
1. What is DNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that forms a twisted ladder shape. Each strand of DNA is composed of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The sequence of these nucleotides along the DNA strand determines the genetic code of an organism.
2. What is RNA?
RNA is a single-stranded molecule that plays a vital role in protein synthesis and other cellular functions. It is similar to DNA in structure, but it has a different composition. RNA is composed of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
3. What is the genetic code?
The genetic code is the sequence of nucleotides in DNA that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins. Proteins are essential for the structure and function of cells. The genetic code is universal, meaning that the same genetic code is used by all organisms on Earth.
4. What is DNA replication?
DNA replication is the process by which DNA