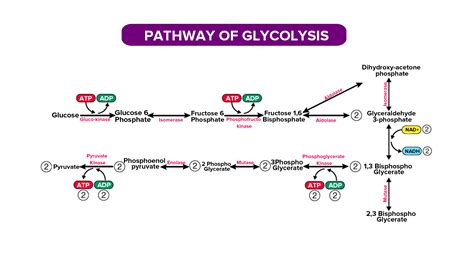
Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration, the process by which cells generate energy. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, and two molecules of ATP are generated. The ATP generated during glycolysis is used to power the rest of cellular respiration, which generates even more ATP.

How is ATP Generated During Glycolysis?
The ATP generated during glycolysis is generated by two different mechanisms:
- Substrate-level phosphorylation: In this mechanism, an enzyme called phosphoglycerate kinase transfers a phosphate group from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP, generating ATP.
- Oxidative phosphorylation: In this mechanism, the electrons released from glucose during glycolysis are used to reduce NAD+ to NADH. The NADH is then used to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, a process that occurs in the mitochondria.
The Importance of ATP
ATP is the body’s main energy currency. It is used to power all of the cell’s activities, including:
- Muscle contraction
- Nerve impulse transmission
- Active transport of molecules across cell membranes
- Chemical reactions
Without ATP, the cell would not be able to function and would eventually die.
Factors that Affect ATP Production
The amount of ATP generated during glycolysis is affected by a number of factors, including:
- The availability of glucose: The more glucose that is available, the more ATP that can be generated.
- The activity of the enzymes involved in glycolysis: The more active these enzymes are, the more ATP that can be generated.
- The presence of oxygen: Oxygen is required for oxidative phosphorylation, which is the most efficient way to generate ATP. In the absence of oxygen, glycolysis can still generate ATP, but it is less efficient.
Applications of ATP
The ATP generated during glycolysis is used to power a wide range of applications, including:
- Medical devices: ATP is used to power medical devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators.
- Food preservation: ATP is used to preserve food by killing bacteria.
- Industrial processes: ATP is used in a variety of industrial processes, such as papermaking and textile manufacturing.
Conclusion
The ATP generated during glycolysis is essential for life. It is used to power all of the cell’s activities and is used in a wide range of applications. By understanding how ATP is generated during glycolysis, we can develop new ways to use this energy molecule to improve our lives.
What is glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration, the process by which cells generate energy. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, and two molecules of ATP are generated.
How is ATP generated during glycolysis?
The ATP generated during glycolysis is generated by two different mechanisms: substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the importance of ATP?
ATP is the body’s main energy currency. It is used to power all of the cell’s activities, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, active transport of molecules across cell membranes, and chemical reactions.
What factors affect ATP production?
The amount of ATP generated during glycolysis is affected by a number of factors, including the availability of glucose, the activity of the enzymes involved in glycolysis, and the presence of oxygen.
What are some applications of ATP?
The ATP generated during glycolysis is used to power a wide range of applications, including medical devices, food preservation, and industrial processes.