Introduction
Psychiatry, the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders, is a complex and ever-evolving field. In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on the importance of personalized treatment plans that take into account the individual needs of each patient. The 4 P’s of psychiatry provide a framework for clinicians to develop effective and tailored treatment plans for their patients.

Assessment
The first step in psychiatric treatment is a thorough assessment of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and social history. This assessment should include a clinical interview, a physical examination, and a review of the patient’s medical records. The clinician may also order laboratory tests or imaging studies to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the patient’s symptoms.
Problem Definition
Once the clinician has completed the assessment, they will work with the patient to define the problem. This involves identifying the specific symptoms that are causing the patient distress and determining the underlying causes of these symptoms. The clinician will also consider the patient’s goals for treatment and their expectations for the outcome.
Plan Development
The next step is to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to the individual needs of the patient. This plan may include a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and other interventions.
Psychotherapy is a type of talk therapy that helps patients to understand and change their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. There are many different types of psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychodynamic therapy, and family therapy.
Medication can be used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. The type of medication that is prescribed will depend on the specific symptoms that the patient is experiencing and their individual needs.
Other interventions that may be included in a treatment plan include lifestyle changes, such as exercise, diet, and sleep hygiene; support groups; and complementary therapies, such as yoga and mindfulness meditation.
Evaluation and Follow-Up
It is important to regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make adjustments as needed. This may involve monitoring the patient’s symptoms, reviewing their progress towards their goals, and making changes to the treatment plan based on the patient’s feedback.
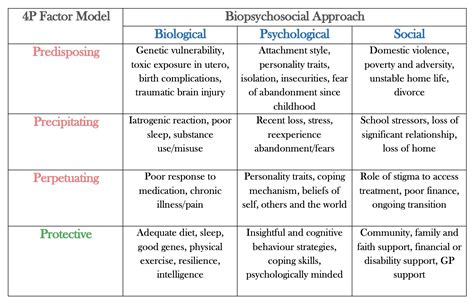
The 4 P’s of psychiatry can be broken down into four key components:
1. Person
The person is the individual who is experiencing the mental health condition. The clinician should consider the patient’s unique needs, values, and preferences when developing a treatment plan.
2. Problem
The problem is the specific mental health condition that the patient is experiencing. The clinician should clearly define the problem and understand its underlying causes in order to develop an effective treatment plan.
3. Plan
The plan is the treatment plan that the clinician develops for the patient. The plan should be tailored to the individual needs of the patient and should include a combination of interventions that are likely to be effective.
4. Process
The process is the ongoing process of evaluation and follow-up that the clinician uses to monitor the patient’s progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
Effective Strategies:
- Use a collaborative approach. The clinician should work with the patient to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their individual needs and goals.
- Consider the whole person. The clinician should consider the patient’s physical, psychological, and social needs when developing a treatment plan.
- Set realistic goals. The clinician should work with the patient to set realistic goals for treatment.
- Monitor progress regularly. The clinician should regularly monitor the patient’s progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Failing to consider the whole person. The clinician should not focus solely on the patient’s symptoms; they should also consider the patient’s physical, psychological, and social needs.
- Setting unrealistic goals. The clinician should not set unrealistic goals for treatment. This can lead to disappointment and discouragement.
- Not monitoring progress regularly. The clinician should not fail to regularly monitor the patient’s progress. This can lead to the patient not getting the best possible care.
Step-by-Step Approach:
- Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and social history.
- Problem Definition: Work with the patient to define the problem and identify the underlying causes of their symptoms.
- Plan Development: Develop a treatment plan that is tailored to the individual needs of the patient.
- Evaluation and Follow-Up: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make adjustments as needed.
The 4 P’s of psychiatry provide a framework for clinicians to develop effective and tailored treatment plans for their patients. By considering the person, the problem, the plan, and the process, clinicians can improve the outcomes for patients with mental health conditions.
- The National Institute of Mental Health
- The American Psychiatric Association
- The World Health Organization