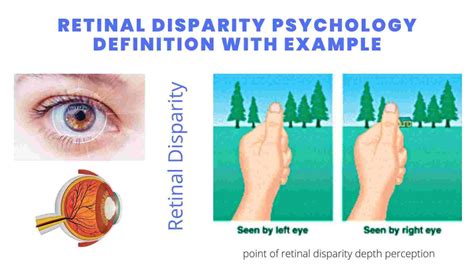
Retinal disparity is a fundamental concept in binocular vision, referring to the slight difference in the images captured by each eye. It plays a crucial role in depth perception, allowing us to perceive the world in three dimensions.

How Retinal Disparity Works
When we look at an object, the angle at which its image falls on the retina of each eye is slightly different. This difference, known as retinal disparity, is directly proportional to the distance of the object from us. Therefore, our brain can use retinal disparity to triangulate the location of objects in space and create a depth map of our surroundings.
The magnitude of retinal disparity depends on the following factors:
- Object distance: Farther objects produce smaller retinal disparity.
- Eye separation: Individuals with larger interpupillary distance (the distance between the two pupils) experience greater retinal disparity for the same object distance.
- Convergence angle: The angle at which the two eyes converge towards the object also influences retinal disparity.
Role in Depth Perception
Retinal disparity is the primary cue for stereoscopic depth perception. It provides a reliable and precise way to determine depth, especially at close distances (within a few meters). Binocular disparity detectors in the visual cortex of the brain process the disparity signals from the two eyes and use them to compute depth information.
Applications in Technology
Retinal disparity has found numerous applications in technology, such as:
- 3D Vision Systems: Stereoscopic displays and virtual reality headsets use retinal disparity to create the illusion of depth.
- Object Tracking: Retinal disparity can be used to track objects in space, enabling applications such as motion capture and augmented reality.
- Biometrics: Retinal disparity can be used for facial recognition and iris scanning, as it provides a unique and stable biometric identifier.
Pain Points and Motivations
- Convergence Insufficiency: Some individuals have difficulty converging their eyes, which can lead to reduced retinal disparity and poor depth perception.
- Motion Sickness: Prolonged exposure to stereoscopic displays that produce large retinal disparity can cause motion sickness in some people.
- Accuracy Limitations: Retinal disparity is less accurate for distant objects, as the disparity becomes too small to be effectively detected.
Why Retinal Disparity Matters
- Enhanced Spatial Awareness: Retinal disparity provides a crucial depth cue, enabling us to navigate our environment safely and efficiently.
- Improved Object Recognition: Depth perception helps us recognize objects more quickly and accurately.
- Enhanced Visual Experience: Stereoscopic displays and virtual reality headsets use retinal disparity to create a more immersive and realistic visual experience.
Tips and Tricks
- Practice Binocular Vision: Participate in activities that stimulate binocular vision, such as playing catch or using stereoscopic viewers.
- Check for Convergence Insufficiency: If you experience difficulty with depth perception, consult an eye care professional to check for convergence insufficiency.
- Use a Stereoscope: Use a stereoscope to view stereoscopic photographs or videos, which can help improve depth perception and train the brain to use retinal disparity effectively.
Benefits of Retinal Disparity
- Accurate Depth Perception: Retinal disparity provides the most precise and reliable depth cue, allowing us to judge distances accurately.
- Improved Visual Comfort: By reducing the demand on accommodation (the ability to focus the lens), retinal disparity enhances visual comfort during near-work activities.
- Enhanced Safety: Depth perception is essential for avoiding obstacles, navigating slopes, and performing tasks that require precise hand-eye coordination.
Conclusion
Retinal disparity is a key physiological mechanism that allows us to perceive depth and experience the world in three dimensions. Its importance in depth perception, visual comfort, and technological applications cannot be overstated. Continued research in this area holds promise for further advancements in visual technology and understanding of human vision.
Table 1: Factors Affecting Retinal Disparity
| Factor | Effect |
|---|---|
| Object Distance | Farther objects produce smaller disparity |
| Eye Separation | Larger separation produces greater disparity |
| Convergence Angle | Greater convergence angle increases disparity |
Table 2: Applications of Retinal Disparity
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| 3D Vision Systems | Creates the illusion of depth in stereoscopic displays and VR headsets |
| Object Tracking | Enables precise tracking of objects in space |
| Biometrics | Used for facial recognition and iris scanning |
Table 3: Pain Points Related to Retinal Disparity
| Pain Point | Impact |
|---|---|
| Convergence Insufficiency | Difficulty converging eyes, reducing depth perception |
| Motion Sickness | Prolonged exposure to large retinal disparity can cause nausea |
| Accuracy Limitations | Reduced accuracy for distant objects |
Table 4: Benefits of Retinal Disparity
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Accurate Depth Perception | Enables precise judgment of distances |
| Improved Visual Comfort | Reduces demand on accommodation, enhancing visual comfort |
| Enhanced Safety | Essential for obstacle avoidance and hand-eye coordination tasks |