Introduction
In various sectors, including education, healthcare, and manufacturing, raw results grades serve as an essential tool for assessing performance. They provide a concrete and quantifiable measure of success or failure, enabling stakeholders to identify areas of strength and weakness. This guide delves into the complexities of raw results grades, exploring their benefits, limitations, and implications.

Understanding Raw Results Grades
Raw results grades are numerical values assigned to a performance measure without any adjustment or modification. They represent the unprocessed data collected from assessments, evaluations, or measurements. These grades provide a direct indication of a candidate’s or organization’s performance on specific tasks or criteria.
Importance of Raw Results Grades
Raw results grades serve several crucial functions:
- Objective Assessment: They offer a standardized and unbiased measure of performance, eliminating subjective influences and ensuring fair evaluation.
- Identification of Strengths and Weaknesses: By comparing raw results grades across different individuals or entities, stakeholders can pinpoint areas where individuals or organizations excel and areas that require improvement.
- Accountability: They promote accountability by providing clear evidence of performance, encouraging individuals or organizations to take ownership of their results.
- Benchmarking: Raw results grades enable benchmarking against internal or external standards, allowing for comparisons with competitors or industry best practices.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While raw results grades offer valuable insights, certain pitfalls should be avoided to ensure their accurate interpretation:
- Overreliance: Solely relying on raw results grades can lead to a narrow understanding of performance. Other factors, such as effort, potential, and context, should also be considered.
- Ignoring Context: Raw results grades should not be interpreted in isolation. The context in which they are collected, such as difficulty level or environmental factors, should be taken into account.
- Unfair Comparisons: Comparing raw results grades across different individuals or entities without considering factors such as age, experience, or background can be misleading.
- Bias: Prejudice or favoritism can influence raw results grades, potentially skewing their accuracy.
Benefits of Raw Results Grades
Raw results grades offer several tangible benefits:
- Transparency: They provide clear and accessible information about performance, fostering transparency and accountability.
- Motivation: They incentivize individuals or organizations to improve their performance by setting measurable targets and providing feedback.
- Performance Improvement: By identifying areas of weakness, raw results grades facilitate the development of improvement strategies and interventions.
- Resource Allocation: They assist in prioritizing resources and targeting support to areas where they are most needed.
Applications of Raw Results Grades
Raw results grades find applications in various domains:
- Education: Assessing student performance on assignments, tests, and exams.
- Healthcare: Evaluating patient outcomes, such as recovery rates and treatment effectiveness.
- Manufacturing: Measuring product quality, production efficiency, and scrap rates.
- Business: Assessing employee performance, customer satisfaction, and financial metrics.
Informative Tables
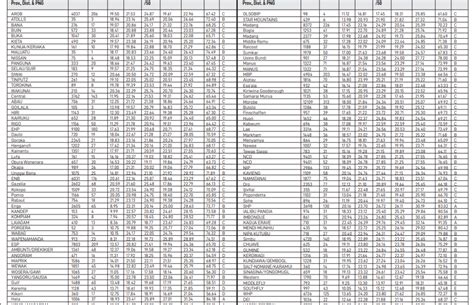
Table 1: Examples of Raw Results Grades
| Performance Measure | Raw Results Grade |
|---|---|
| Student Test Score | 87% |
| Patient Recovery Time | 5 days |
| Product Defect Rate | 1% |
| Employee Sales Target | 120% |
Table 2: Common Mistakes to Avoid in Interpreting Raw Results Grades
| Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
| Overreliance | Solely relying on raw results grades without considering other factors. |
| Ignoring Context | Failing to take into account the context in which raw results grades are collected. |
| Unfair Comparisons | Comparing raw results grades across different individuals or entities without considering relevant factors. |
| Bias | Prejudice or favoritism influencing raw results grades. |
Table 3: Benefits of Raw Results Grades
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Transparency | Providing clear and accessible information about performance. |
| Motivation | Incentivizing individuals or organizations to improve performance. |
| Performance Improvement | Identifying areas of weakness and facilitating improvement strategies. |
| Resource Allocation | Assisting in prioritizing resources and targeting support where needed. |
Table 4: Applications of Raw Results Grades
| Domain | Examples |
|---|---|
| Education | Student performance assessment, grading |
| Healthcare | Patient outcomes evaluation |
| Manufacturing | Product quality and efficiency measurement |
| Business | Employee performance evaluation, customer satisfaction assessment |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between raw and adjusted results grades?
A1: Raw results grades are unprocessed values, while adjusted results grades have been modified to account for factors such as difficulty level or external influences.
Q2: How can raw results grades be used to improve performance?
A2: By identifying areas of weakness, raw results grades enable the development of targeted interventions and improvement strategies.
Q3: What are some creative applications of raw results grades?
A3: Raw results grades can be used to develop predictive models, identify trends, and optimize processes in various industries.
Q4: How can bias be minimized in raw results grades?
A4: Implementing standardized grading criteria, using multiple assessors, and providing training on bias reduction can help minimize bias.
Q5: What are the limitations of raw results grades?
A5: Raw results grades can be influenced by factors beyond the individual’s or organization’s control, and they may not reflect the overall quality of performance.
Q6: How do raw results grades compare to qualitative evaluations?
A6: Qualitative evaluations provide subjective insights and context, while raw results grades offer standardized and quantifiable measures. Both methods are valuable for comprehensive performance assessment.
Q7: What is the role of technology in raw results grades?
A7: Technology can automate data collection, facilitate analysis, and enhance the accuracy and efficiency of raw results grades.
Q8: How can raw results grades be used ethically?
A8: Raw results grades should be used fairly, transparently, and in a way that protects individual privacy and promotes equitable outcomes.