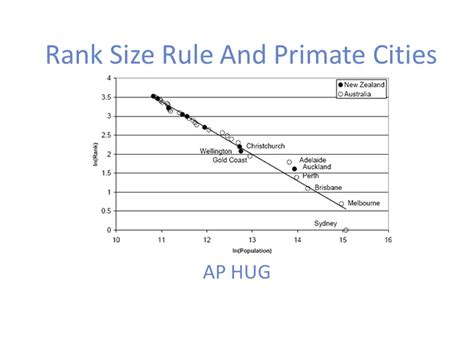
Introduction

The rank-size rule is a fundamental concept in urban geography that describes the relationship between the population size of cities and their ranks. It states that the population of a city is inversely proportional to its rank in the urban system, meaning that the largest city in a region will have the most people, the second largest city will have the second most people, and so on.
This relationship has been observed in many different regions of the world, and it holds true for both developed and developing countries. However, there are some exceptions to the rule, particularly in small and isolated regions.
Mathematical Formula
The rank-size rule can be expressed mathematically as follows:
P = k / R^b
Where:
- P is the population of the city
- k is a constant that varies depending on the region being studied
- R is the rank of the city in the urban system
- b is a constant that is typically between 0.5 and 1.0
Applications of the Rank-Size Rule
The rank-size rule has a number of applications in urban planning and geography. It can be used to:
- Predict the population of a city based on its rank
- Compare the size of different cities in a region
- Identify potential growth centers
- Plan for infrastructure and services
Limitations of the Rank-Size Rule
The rank-size rule is a useful tool for understanding the relationship between the size of cities and their ranks. However, it is important to note that there are some limitations to the rule.
- The rule does not apply to all regions of the world.
- The rule does not account for the effects of history, geography, or economic development.
- The rule does not apply to small or isolated cities.
Conclusion
The rank-size rule is a useful tool for understanding the relationship between the size of cities and their ranks. However, it is important to note that there are some limitations to the rule. When used in conjunction with other data, the rank-size rule can be a valuable tool for urban planning and geography.
The following tables provide data on the population of cities in the United States and the world.
| Rank | City | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | New York City | 8,804,190 |
| 2 | Los Angeles | 3,990,456 |
| 3 | Chicago | 2,746,388 |
| 4 | Houston | 2,304,580 |
| 5 | Philadelphia | 1,608,161 |
| Rank | City | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tokyo | 37,339,804 |
| 2 | Delhi | 28,514,000 |
| 3 | Shanghai | 26,319,000 |
| 4 | Beijing | 21,542,000 |
| 5 | São Paulo | 21,650,000 |
Here are some tips and tricks for using the rank-size rule:
- Use the rule to predict the population of a city based on its rank.
- Compare the size of different cities in a region using the rule.
- Identify potential growth centers using the rule.
- Plan for infrastructure and services using the rule.
The rank-size rule matters because it can help us to understand the relationship between the size of cities and their ranks. This information can be used to plan for infrastructure and services, and to identify potential growth centers.
There are a number of benefits to using the rank-size rule. These benefits include:
- The rule is simple to use and understand.
- The rule can be applied to any region of the world.
- The rule can provide valuable insights into the relationship between the size of cities and their ranks.