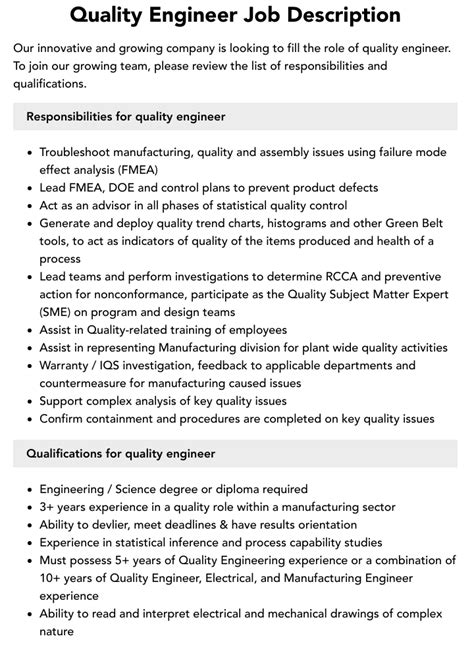
As a quality engineer intern, you’ll step into a dynamic and multifaceted role where you’ll play a pivotal role in ensuring the quality, safety, and reliability of products and services. Embark on a journey of continuous improvement and contribute to the success of organizations in various industries.

Your responsibilities as a quality engineer intern may include:
- Assisting with quality planning and implementing quality assurance processes
- Conducting inspections, audits, and tests to verify compliance with quality standards
- Analyzing data to identify areas for improvement and develop corrective actions
- Collaborating with engineers, production teams, and customers to address quality concerns
- Participating in the design and execution of quality management systems (QMS)
To succeed as a quality engineer intern, you should possess:
- Strong understanding of quality principles and methodologies
- Knowledge of statistical methods and data analysis techniques
- Excellent analytical and problem-solving abilities
- Proficiency in software tools for quality management
- Effective communication and interpersonal skills
- Ability to work independently and as part of a team
Quality engineers are sought after in a wide range of industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices
- Technology: Software development, hardware manufacturing, IT services
- Healthcare: Hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, medical equipment manufacturers
- Food and Beverage: Production, distribution, retail
- Aerospace: Aircraft manufacturing, airline operations
Interning as a quality engineer offers numerous benefits, such as:
- Gaining hands-on experience in the field of quality engineering
- Developing a strong understanding of quality management principles
- Building a network of professionals in the industry
- Contributing to the success of organizations and improving the quality of products and services
- Preparing for a rewarding career in quality engineering
With experience and expertise, quality engineer interns can progress to roles such as:
- Quality Engineer
- Quality Manager
- Director of Quality
- Vice President of Quality
- Ask Questions: Engage with experienced professionals and seek their insights.
- Stay Up-to-Date: Attend industry events, read publications, and pursue continuous learning.
- Validate Customers’ Perspectives: Gather feedback and actively listen to understand their needs and expectations.
- Use Innovation to Generate Ideas: Explore new technologies and approaches to improve quality processes.
Pros:
- Hands-on experience in a critical field
- Opportunity for professional growth
- Potential for a rewarding career
- Positive impact on organizations and customers
Cons:
- Can be demanding and require a high level of attention to detail
- May involve working with complex technical systems
- Can be repetitive at times
Quality engineers face various challenges, including:
- Complexity of Modern Products: With the increasing sophistication of products, ensuring quality becomes more complex.
- Global Supply Chains: Managing quality across global supply chains requires effective coordination and oversight.
- Regulatory Requirements: Adhering to stringent regulatory requirements is essential to avoid penalties and ensure public safety.
Despite these challenges, quality engineering offers ample opportunities for innovation and continuous improvement.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for quality engineers was $94,230 in May 2021. The job outlook for quality engineers is projected to grow 4% from 2021 to 2031, about as fast as the average for all occupations.
| Standard | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | International quality management system standard | Manufacturing, healthcare, technology |
| AS9100 | Aerospace quality management system standard | Aerospace industry |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 11 | Electronic records and electronic signatures in the pharmaceutical industry | Pharmaceutical development |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental management system standard | All industries with environmental concerns |
| Tool/Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) | Identifies potential failure modes and their consequences | Reduces risk, improves reliability |
| Statistical Process Control (SPC) | Monitors and controls production processes | Improves quality, reduces variability |
| Six Sigma | Methodology for improving processes and reducing defects | Eliminates waste, increases efficiency |
| Lean Manufacturing | Eliminates waste and improves efficiency | Reduces costs, improves productivity |
| Industry | Percentage of Quality Engineers |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 25% |
| Healthcare | 20% |
| Technology | 15% |
| Food and Beverage | 10% |
| Aerospace | 5% |
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Quality Engineer | Implement quality assurance processes, conduct inspections |
| Quality Manager | Oversee quality management systems, manage team |
| Director of Quality | Develop and implement quality strategies, report to senior management |
| Vice President of Quality | Lead quality initiatives across the organization, ensure compliance |