In the realm of data analysis, the distinction between populations and samples holds immense significance, particularly in the context of media applications. Understanding this concept is crucial for making informed decisions about data collection and interpretation.

Populations vs Samples: A Breakdown
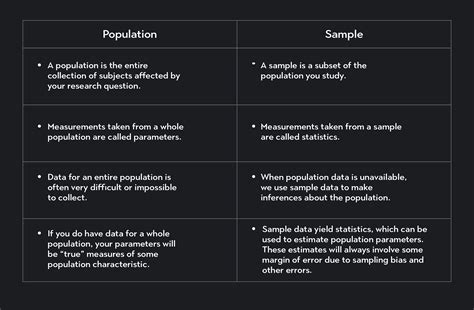
Population: A population encompasses the entire set of individuals or entities being studied. It represents the totality of the group under consideration.
Sample: A sample is a subset of the population that is selected to represent the larger group. Researchers use samples to make inferences about the entire population.
The Power of Samples in Media Apps
Media apps leverage samples to gain valuable insights about their target audiences. By analyzing data from a sample of users, they can:
- Understand user behavior: Track user engagement, preferences, and usage patterns to optimize app functionality and content.
- Identify trends: Spot emerging trends and patterns in user demographics, interests, and behavior.
- Personalize experiences: Tailor content and recommendations to individual users based on their sample data.
- Measure effectiveness: Evaluate the impact of marketing campaigns, app updates, and other interventions.
Data Collection from Samples
Media apps typically collect data from samples through methods such as:
- Surveys: Send questionnaires to users to gather feedback and insights.
- Analytics: Track user behavior within the app to collect data on usage patterns.
- A/B testing: Split users into groups and expose them to different versions of the app or content to test effectiveness.
Importance of Representative Samples
The accuracy of inferences made from samples depends on their representativeness. Researchers must ensure that the sample accurately reflects the characteristics of the target population. This can be achieved through:
- Random sampling: Selecting subjects randomly to avoid bias.
- Stratified sampling: Dividing the population into subgroups (e.g., demographics) and randomly selecting subjects from each subgroup.
Creative Applications for Media Apps
Leveraging the concept of populations and samples unlocks opportunities for innovative media app applications:
- Audience segmentation: Divide users into segments based on sample data to deliver targeted content and advertising.
- Predictive analytics: Use machine learning algorithms to predict user behavior and preferences based on sample data.
- Micro-targeting: Personalize content and experiences for individual users based on their unique data profile.
Tables for Populations and Samples
| Table 1: Population vs Sample Characteristics | Table 2: Methods of Sample Selection | Table 3: Importance of Representative Samples | Table 4: Innovative Media App Applications Using Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population | Sample | Importance | Applications |
| ——————– | —————— | ————————— | ———————————————————- |
| Entire group under consideration | Subset representing the group | Accurate inferences | Audience segmentation |
| Represents the totality | Provides insights | Avoids bias | Predictive analytics |
| Can be large or small | Helps determine trends | Ensures generalizability | Micro-targeting |
FAQs
Q: Why are samples used instead of studying the entire population?
A: Studying the entire population can be impractical or impossible. Samples provide a cost-effective and efficient way to make inferences.
Q: How do I ensure the representativeness of my sample?
A: Use random sampling or stratified sampling to select subjects that accurately reflect the characteristics of the target population.
Q: What is the difference between a biased and an unbiased sample?
A: A biased sample is one that does not accurately represent the target population, while an unbiased sample does.
Q: Can I use a sample to make conclusions about the population?
A: Yes, with caution. While samples provide valuable insights, the inferences must be interpreted with regard to the limitations of the sample size and representativeness.
Conclusion
Understanding the concepts of populations and samples is vital for media apps. By leveraging samples to extract insights and make informed decisions, media apps can optimize user experiences, personalize content, and measure effectiveness. The creative applications for samples in media apps are endless, opening up new possibilities for innovation and engagement.