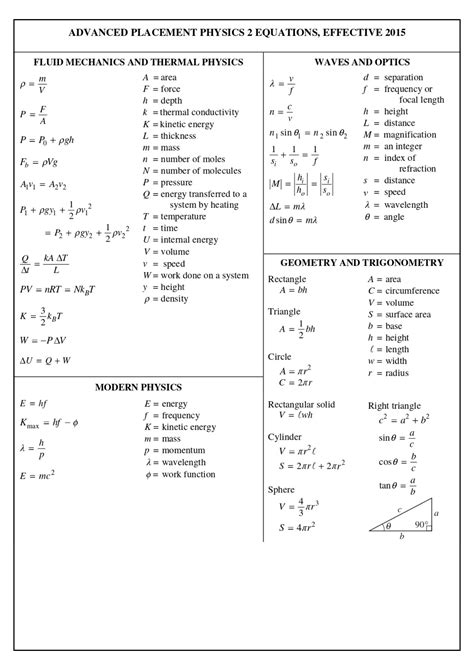
Introduction

Physics II, also known as Advanced Physics, builds upon the concepts from Physics I and explores more complex topics in mechanics, thermodynamics, waves, and electromagnetism. This comprehensive equation sheet provides a concise summary of essential formulas and equations that will guide you through your Physics II journey.
Kinematics
- Position: x = x₀ + v₀t + ½at²
- Velocity: v = v₀ + at
- Acceleration: a = (vf – v₀) / t
- Constant Acceleration: v² = v₀² + 2ax
Dynamics
- Newton’s Second Law: F = ma
- Gravitational Force: F = Gm₁m₂ / r²
- Conservation of Momentum: p₁ = p₂
- Impulse: J = Δp = Ft
Circular Motion
- Centripetal Force: F = mv²/r
- Period: T = 2πr / v
- Frequency: f = 1 / T
Thermodynamics
- First Law of Thermodynamics: Q = ΔU + W
- Specific Heat Capacity: Q = mcΔT
-
Gas Laws:
- Boyle’s Law: P₁V₁ = P₂V₂ (constant temperature)
- Charles’s Law: V₁ / T₁ = V₂ / T₂ (constant pressure)
- Combined Gas Law: P₁V₁ / T₁ = P₂V₂ / T₂
Waves
- Wave Velocity: v = fλ
- Frequency: f = 1 / T
- Wavelength: λ = v / f
- Doppler Effect (Moving Source): f’ = f(v + v₀) / (v + vs)
- Doppler Effect (Moving Observer): f’ = f(v – v₀) / (v – vs)
Electromagnetism
- Coulomb’s Law: F = kq₁q₂ / r²
- Electric Field: E = kq / r²
- Gauss’s Law: ∮E·dA = Q / ε₀
- Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge: F = qvBsinθ
- Magnetic Field of a Current Carrying Wire: B = μ₀I / 2πr
Modern Physics
- Planck’s Constant: h = 6.63 x 10^-34 J s
- Photoelectric Effect: E = hf – Φ
- De Broglie Wavelength: λ = h / p
Tables
| Table 1: Constants | Value |
|---|---|
| Gravitational Constant (G) | 6.67 x 10^-11 N m² kg^-2 |
| Coulomb’s Constant (k) | 9.0 x 10^9 N m² C^-2 |
| Permittivity of Free Space (ε₀) | 8.85 x 10^-12 C² N^-1 m^-2 |
| Permeability of Free Space (μ₀) | 4π x 10^-7 T m A^-1 |
| Planck’s Constant (h) | 6.63 x 10^-34 J s |
| Table 2: Prefixes | Symbol | Multiplier |
|---|---|---|
| Tera | T | 10^12 |
| Giga | G | 10^9 |
| Mega | M | 10^6 |
| Kilo | k | 10^3 |
| Centi | c | 10^-2 |
| Milli | m | 10^-3 |
| Micro | μ | 10^-6 |
| Nano | n | 10^-9 |
| Pico | p | 10^-12 |
| Table 3: Common Functions | Equation |
|---|---|
| Sine | sin(θ) |
| Cosine | cos(θ) |
| Tangent | tan(θ) |
| Inverse Sine | sin^-1(x) |
| Inverse Cosine | cos^-1(x) |
| Inverse Tangent | tan^-1(x) |
| Table 4: Units of Measurement | Quantity | SI Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | Meter (m) | |
| Mass | Kilogram (kg) | |
| Time | Second (s) | |
| Force | Newton (N) | |
| Energy | Joule (J) | |
| Power | Watt (W) | |
| Electric Charge | Coulomb (C) | |
| Electric Potential | Volt (V) | |
| Magnetic Flux | Weber (Wb) |
Applications of Physics II
Physics II has innumerable applications in various industries and fields, including:
- Engineering: Design and optimization of bridges, buildings, vehicles, and other structures
- Biophysics: Study of biological processes, medical imaging, and drug development
- Astronomy: Exploration of stars, planets, and galaxies
- Robotics: Development of autonomous vehicles, drones, and other automated systems
- Quantum Computing: Advancements in computing power and information processing
Conclusion
This comprehensive Physics II equation sheet captures the core concepts and essential equations of the subject. By mastering these formulas, you will not only excel in your studies but also gain a deeper understanding of the physical world around you. Remember to practice applying these equations regularly and seek guidance from your instructor or tutor whenever necessary. May this sheet serve as a constant companion on your Physics II journey.