1. Kinematics

- Displacement: Δx = x_f – x_i
- Velocity: v = Δx/Δt
- Acceleration: a = Δv/Δt
- Constant acceleration: v = v_i + at
- Constant acceleration: Δx = v_it + 1/2a*t^2
- Constant acceleration: v^2 = v_i^2 + 2aΔx
2. Force and Motion
- Newton’s second law: F = ma
- Weight: F_g = mg
- Friction: F_f = μ*N
- Normal force: N = F_g – F_f
- Tension: T = F_net
3. Work and Energy
- Work: W = F*d
- Kinetic energy: K = 1/2*mv^2
- Potential energy: U = mgh
- Conservation of energy: ΔK + ΔU = 0
4. Momentum
- Momentum: p = mv
- Impulse: J = Δp
- Conservation of momentum: p_i = p_f
5. Rotational Motion
- Angular displacement: θ = Δθ/Δt
- Angular velocity: ω = Δθ/Δt
- Angular acceleration: α = Δω/Δt
- Rotational inertia: I = Σmr^2
- Torque: τ = Iα
6. Fluid Mechanics
- Density: ρ = m/V
- Pressure: P = F/A
- Archimedes’ principle: F_b = ρgV_d
- Bernoulli’s principle: P + 1/2ρv^2 = constant
7. Heat and Thermodynamics
- Heat transfer: Q = mcΔT
- Specific heat: c = Q/(mΔT)
- Thermal conductivity: k = Q/(AtΔT)
- Ideal gas law: PV = nRT
- First law of thermodynamics: ΔU = Q – W
8. Waves
- Wave speed: v = fλ
- Frequency: f = 1/T
- Wavelength: λ = v/f
- Doppler effect: f_o = f_s(v ± v_o)/(v ± v_s)
9. Optics
- Speed of light: c = 3 x 10^8 m/s
- Index of refraction: n = c/v
- Snell’s law: n_1sinθ_1 = n_2sinθ_2
- Lens equation: 1/f = 1/d_o + 1/d_i
10. Electricity and Magnetism
- Coulomb’s law: F = kq_1q_2/r^2
- Electric field: E = kq/r^2
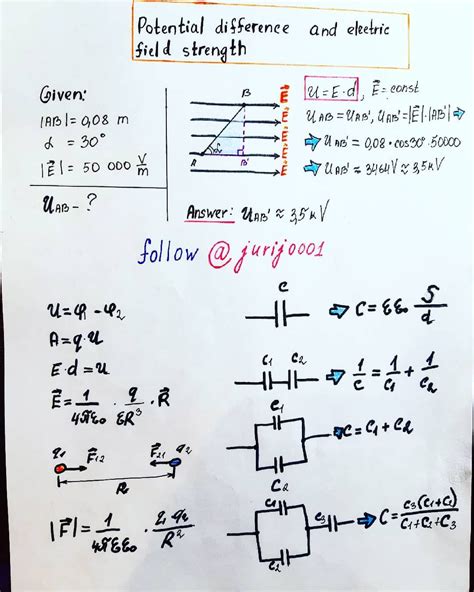
- Potential difference: V = Ed
- Resistance: R = V/I
- Ohm’s law: V = IR
- Magnetic field: B = μ_0I/2πr
- Lorentz force: F = q(E + v x B)
Tables
Table 1: Constants
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| Speed of light | 3 x 10^8 m/s |
| Gravitational constant | 6.674 x 10^-11 N m^2/kg^2 |
| Coulomb constant | 8.988 x 10^9 N m^2/C^2 |
| Magnetic constant | 4π x 10^-7 T m/A |
Table 2: SI Units
| Quantity | Unit |
|---|---|
| Length | Meter (m) |
| Mass | Kilogram (kg) |
| Time | Second (s) |
| Electric charge | Coulomb (C) |
| Current | Ampere (A) |
| Temperature | Kelvin (K) |
Table 3: Prefixes
| Prefix | Symbol | Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Giga | G | 10^9 |
| Mega | M | 10^6 |
| Kilo | k | 10^3 |
| Milli | m | 10^-3 |
| Micro | μ | 10^-6 |
| Nano | n | 10^-9 |
Table 4: Conversions
| From | To | Multiply by |
|---|---|---|
| Meter | Inch | 39.37 |
| Kilogram | Pound | 2.205 |
| Second | Hour | 1/3600 |
| Coulomb | Electron charge | 1.602 x 10^-19 |
| Ampere | Milliampere | 1000 |
| Kelvin | Fahrenheit | (K – 273.15) x 1.8 + 32 |
Applications of Physics
- Automotive engineering
- Aerospace engineering
- Civil engineering
- Medical physics
- Astrophysics
- Geophysics
- Computer science
- Energy production
- Environmental science
- Materials science
Effective Strategies for Studying Physics
- Attend lectures and take detailed notes
- Read the textbook and solve practice problems
- Participate in class discussions and ask questions
- Form study groups with classmates
- Seek help from your instructor or a tutor
- Use online resources and simulations
- Review material regularly and summarize key concepts
Tips and Tricks
- Break down complex problems into smaller steps
- Use diagrams and sketches to visualize concepts
- Derive formulas rather than memorizing them
- Use dimensional analysis to check your work
- Be patient and don’t give up easily
FAQs
-
What is the most important concept in physics?
– The principle of causality. -
What are the different branches of physics?
– Mechanics, heat and thermodynamics, waves, optics, electricity and magnetism, and nuclear physics. -
How can I get better at solving physics problems?
– Practice regularly, use dimensional analysis, and refer to your notes. -
What are some common misconceptions in physics?
– Gravity is a force, heat is a fluid, and light is a particle. -
How can I prepare for the Physics GRE?
– Study the formula sheet, solve practice problems, and take mock exams. -
What are some exciting new applications of physics?
– Quantum computing, nanotechnology, and artificial intelligence.