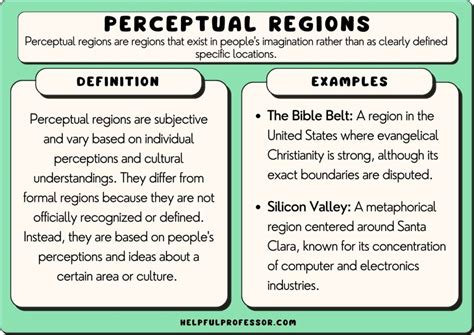
Perceptual regions: are areas defined by people’s perceptions, rather than by objective physical or cultural characteristics. They are often based on shared experiences, common history or identity and values. Perceptual regions can be large or small, and can change over time.

There are many different types of perceptual regions. Examples include:
- Cultural regions
- Economic regions
- Political regions
- Religious regions
- Ethnic regions
- Linguistic regions
Cultural regions: are defined by shared cultural traits, such as language, religion, customs, and traditions. For example, the Middle East is a cultural region that is characterized by the Arabic language, Islam, and a rich history of trade and commerce.
Economic regions: are defined by shared economic activities. For example, the Rust Belt is an economic region in the United States that was once a major center of manufacturing.
Political regions: are defined by shared political boundaries. For example, the United States is a political region that is divided into 50 states.
Religious regions: are defined by shared religious beliefs. For example, the Bible Belt is a religious region in the United States that is characterized by a high concentration of Protestant Christians.
Ethnic regions: are defined by shared ethnicity. For example, the Basque Country is an ethnic region in Spain that is home to the Basque people.
Linguistic regions: are defined by shared language. For example, the French-speaking region of Canada is a linguistic region that is home to people who speak French.
Perceptual regions are important because they can help us to understand how people identify with their surroundings and how they interact with others. They can also be used to explain the distribution of economic activity, political power, and cultural diversity across the globe.
Perceptual regions: are important for a number of reasons. First, they can help us to understand how people identify with their surroundings. For example, a person who lives in the American South may identify with the South as a cultural region, and may share the values and beliefs of other Southerners.
Second, perceptual regions can help us to understand how people interact with others. For example, people who live in different cultural regions may have different ways of communicating, behaving, and thinking. Understanding these differences can help us to avoid misunderstandings and build strong relationships with people from other cultures.
Third, perceptual regions can help us to explain the distribution of economic activity, political power, and cultural diversity across the globe. For example, the concentration of economic activity in the Northeast United States can be explained, in part, by the region’s history of manufacturing and trade.
There are many benefits to understanding perceptual regions. These benefits include:
- Improved communication: Understanding perceptual regions can help us to communicate more effectively with people from different backgrounds.
- Increased tolerance: Understanding perceptual regions can help us to be more tolerant of people who are different from us.
- Enhanced problem-solving: Understanding perceptual regions can help us to solve problems that are related to cultural diversity.
- Greater global awareness: Understanding perceptual regions can help us to develop a greater understanding of the world and its people.
There are a number of common mistakes to avoid when defining perceptual regions. These mistakes include:
- Assuming that perceptual regions are fixed: Perceptual regions are not fixed, and can change over time. For example, the boundaries of the American South have changed over time as people have migrated to and from the region.
- Ignoring the role of individual perception: Perceptual regions are defined by people’s perceptions, and not by objective physical or cultural characteristics. This means that different people may have different perceptions of the same region.
- Using only one criterion to define perceptual regions: Perceptual regions can be defined using a variety of criteria, including culture, economics, politics, religion, ethnicity, and language. Using only one criterion can lead to a narrow and incomplete definition of the region.
Policymakers: can use perceptual region findings to develop policies that are tailored to the needs of specific regions. For example, policymakers could develop economic development policies that are designed to address the needs of a particular cultural region.
Businesses: can use perceptual region findings to target their marketing and advertising campaigns. For example, a business could develop a marketing campaign that is designed to appeal to the values and beliefs of a particular cultural region.
Educators: can use perceptual region findings to develop educational programs that are relevant to the students in their region. For example, an educator could develop a history curriculum that is focused on the history of the region in which the students live.
Individuals: can use perceptual region findings to better understand their own identity and the identity of others. For example, an individual could learn about the history and culture of their own region, and how it has shaped their own identity.
Perceptual regions are important for a number of reasons. They can help us to understand how people identify with their surroundings, how they interact with others, and how they explain the distribution of economic activity, political power, and cultural diversity across the globe. Understanding perceptual regions can also help us to avoid misunderstandings, build strong relationships, solve problems, and develop a greater understanding of the world and its people.
Table 1: Types of Perceptual Regions
| Type | Definition | Example |
|—|—|—|
| Cultural | Defined by shared cultural traits | Middle East |
| Economic | Defined by shared economic activities | Rust Belt |
| Political | Defined by shared political boundaries | United States |
| Religious | Defined by shared religious beliefs | Bible Belt |
| Ethnic | Defined by shared ethnicity | Basque Country |
| Linguistic | Defined by shared language | French-speaking region of Canada |
Table 2: Benefits of Understanding Perceptual Regions
| Benefit | Description |
|—|—|
| Improved communication | Understanding perceptual regions can help us to communicate more effectively with people from different backgrounds. |
| Increased tolerance | Understanding perceptual regions can help us to be more tolerant of people who are different from us. |
| Enhanced problem-solving | Understanding perceptual regions can help us to solve problems that are related to cultural diversity. |
| Greater global awareness | Understanding perceptual regions can help us to develop a greater understanding of the world and its people. |
Table 3: Common Mistakes to Avoid When Defining Perceptual Regions
| Mistake | Description |
|—|—|
| Assuming that perceptual regions are fixed | Perceptual regions are not fixed, and can change over time. |
| Ignoring the role of individual perception | Perceptual regions are defined by people’s perceptions, and not by objective physical or cultural characteristics. |
| Using only one criterion to define perceptual regions | Perceptual regions can be defined using a variety of criteria, including culture, economics, politics, religion, ethnicity, and language. |
Table 4: Applications of Perceptual Region Findings
| Application | Description |
|—|—|
| Policymaking | Policymakers can use perceptual region findings to develop policies that are tailored to the needs of specific regions. |
| Business | Businesses can use perceptual region findings to target their marketing and advertising campaigns. |
| Education | Educators can use perceptual region findings to develop educational programs that are relevant to the students in their region. |
| Individual understanding | Individuals can use perceptual region findings to better understand their own identity and the identity of others. |