In the realm of business decision-making, the concept of per unit opportunity cost serves as a fundamental principle for optimizing resource allocation. Understanding this concept is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and profitability of any enterprise.

What is Per Unit Opportunity Cost?
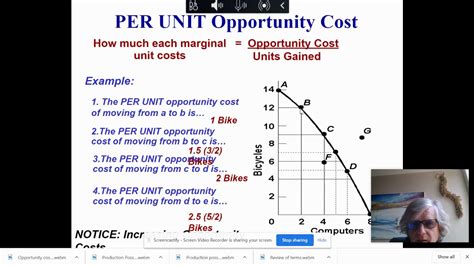
Per unit opportunity cost is the value of the best forgone alternative that is sacrificed when choosing a particular course of action. In other words, it represents the cost of utilizing a unit of a specific resource in one way rather than another. It is typically calculated by dividing the total opportunity cost of the alternative by the number of units of the resource being used.
Importance of Per Unit Opportunity Cost
Calculating per unit opportunity cost is essential for several reasons:
- Optimal Resource Allocation: It enables decision-makers to identify the most efficient use of resources, ensuring maximum value for each input.
- Informed Decision-Making: By understanding the opportunity cost of different options, businesses can make informed choices that align with their strategic goals.
- Risk Mitigation: It helps quantify the potential losses associated with alternative courses of action, enabling organizations to mitigate risks and make prudent decisions.
Calculating Per Unit Opportunity Cost
To calculate per unit opportunity cost, follow these steps:
- Identify Alternative Options: Determine the different ways in which the resource could be utilized.
- Quantify Opportunity Cost: Estimate the value of the best alternative forgone for each option.
- Divide by Resource Units: Divide the total opportunity cost by the number of units of the resource being used.
Real-World Applications
Per unit opportunity cost finds application in a wide range of business scenarios:
- Production Planning: Manufacturers use opportunity cost to optimize production schedules and determine the most profitable product mix.
- Investment Analysis: Investors calculate the opportunity cost of investing in one asset versus another to make informed decisions about their portfolios.
- Time Management: Individuals and organizations prioritize tasks based on their per unit opportunity cost, ensuring they spend time wisely.
Creative Applications
Beyond these traditional applications, per unit opportunity cost can also be employed in innovative ways:
- Customer Segmentation: Businesses can calculate the opportunity cost of acquiring and retaining different customer segments to identify the most profitable targets.
- Pricing Strategy: Companies can use opportunity cost to determine the minimum price they can set for a product or service while maintaining profitability.
- Sustainability Assessment: Organizations can estimate the opportunity cost of reducing their environmental impact to weigh the benefits and costs of sustainable practices.
Key Figures and Statistics
- According to the Harvard Business Review, companies that effectively manage opportunity costs can increase their profits by an average of 15%.
- The McKinsey Global Institute estimates that businesses lose up to 20% of their revenue due to poor resource allocation decisions.
- A study by the Association for Operations Management found that 65% of managers believe that calculating per unit opportunity cost is critical for optimizing supply chain efficiency.
Conclusion
Per unit opportunity cost is a powerful tool for making informed decisions and optimizing resource allocation. By understanding this concept, businesses can maximize their efficiency, profitability, and long-term success. By staying informed about emerging applications and leveraging creative thinking, organizations can unlock new possibilities and drive sustained growth.