Air quality assessment (AAQ) plays a pivotal role in safeguarding public health and environmental sustainability. Selecting appropriate research methods is crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable data in AAQ studies. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the diverse array of methods available, enabling researchers to tailor their investigations to specific research objectives and contexts.

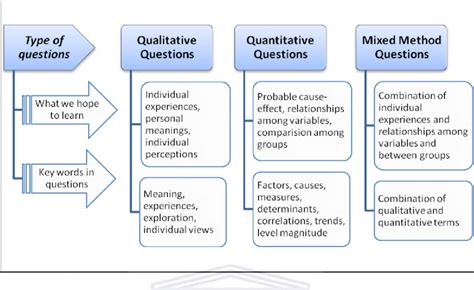
Qualitative methods in AAQ focus on exploring perceptions, experiences, and interpretations related to air pollution. They are particularly valuable for understanding the social and cultural dimensions of air quality issues.
-
Interviews: In-depth interviews allow researchers to gather detailed qualitative data from individual participants. They are often used to explore personal experiences, attitudes, and knowledge regarding air pollution.
-
Focus Groups: Focus groups involve facilitated discussions with small groups of participants. They provide a platform for sharing and comparing perspectives on air quality-related topics.
-
Participant Observation: Researchers directly observe and participate in community activities to gain firsthand insights into air pollution-related behaviors, perceptions, and experiences.
Quantitative methods in AAQ involve the collection and analysis of numerical data to quantify air pollution levels and their impacts.
-
Air Monitoring: Air monitoring stations collect real-time data on concentrations of various air pollutants, including particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), ozone (O3), and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
-
Epidemiological Studies: Epidemiological studies investigate the relationship between air pollution exposure and health outcomes. They typically involve large-scale surveys or cohort studies to identify patterns and quantify associations.
-
Exposure Assessment: Exposure assessment involves measuring the amount of air pollution a person is exposed to over time. This can be done using personal monitors, questionnaires, or dispersion modeling.
-
Modeling and Simulation: Air quality models simulate the transport, dispersion, and chemical reactions of air pollutants. They provide predictions of air pollution concentrations and can be used to forecast future scenarios or evaluate mitigation strategies.
Combining qualitative and quantitative methods can provide a more comprehensive understanding of air pollution issues. For example, a mixed methods approach could involve conducting qualitative interviews to explore community perceptions, followed by quantitative air monitoring to assess actual exposure levels.
Choosing the Right Method
The selection of research methods in AAQ depends on factors such as the research question, available resources, and the desired level of detail. Table 1 summarizes the key considerations for choosing qualitative vs. quantitative methods.
| Qualitative Methods | Quantitative Methods |
|---|---|
| Explore subjective experiences | Measure objective data |
| Understanding perceptions and interpretations | Quantifying levels and impacts |
| Small sample size | Large sample size |
| Rich, in-depth data | Numerical data, statistical analysis |
Advances in technology have facilitated the development of novel techniques for AAQ research.
-
Remote Sensing: Satellite and ground-based sensors collect data on air pollution from a distance. This provides broad-scale coverage and can be used to monitor large areas over time.
-
Citizen Science: Citizen science initiatives involve the public in air quality data collection. This approach can increase the spatial and temporal resolution of air quality data and foster community engagement.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are used to analyze air quality data, identify patterns, and predict future scenarios. This can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of air quality assessments.
AAQ research findings have numerous applications in policy and practice, including:
- Developing air quality regulations and standards
- Targeting pollution reduction strategies
- Assessing the health impacts of air pollution
- Evaluating the effectiveness of air quality interventions
- Improving public awareness and education
- Quantifying the economic costs of air pollution
Investing in AAQ research yields substantial benefits for public health, the environment, and the economy.
- Improved health outcomes: Reducing air pollution can prevent respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, asthma, and premature death.
- Increased economic productivity: Air pollution affects workforce productivity and can lead to absenteeism and presenteeism.
- Environmental benefits: Air pollution damages ecosystems, contributes to climate change, and degrades biodiversity.
- Increased social equity: Air pollution disproportionately affects marginalized communities, and addressing it promotes environmental justice.
- Enhanced community engagement: AAQ research can empower communities to monitor and improve their local air quality.
1. Why is air quality assessment important?
Air quality assessment is crucial for understanding the health and environmental impacts of air pollution and developing effective mitigation strategies.
2. What are the different types of research methods used in AAQ?
AAQ research methods include qualitative methods (interviews, focus groups, participant observation) and quantitative methods (air monitoring, epidemiological studies, exposure assessment, modeling and simulation).
3. How do I choose the right research method for my AAQ study?
Consider factors such as the research question, available resources, and the desired level of detail when selecting a research method.
4. What are the emerging techniques in AAQ research?
Remote sensing, citizen science, and artificial intelligence are emerging techniques that enhance the scope and effectiveness of AAQ research.
5. What are the applications of AAQ research?
AAQ research supports policy and practice in areas such as air quality regulations, pollution reduction strategies, health impact assessment, and public education.
6. What are the benefits of air quality assessment?
Benefits of AAQ include improved health outcomes, increased economic productivity, environmental benefits, increased social equity, and enhanced community engagement.
7. How can I get involved in AAQ research?
Researchers, students, and community organizations can participate in AAQ research by conducting studies, joining research teams, or supporting citizen science initiatives.
8. What are the challenges and limitations of AAQ research?
Challenges include data availability, methodological limitations, and the complexity of air pollution sources and impacts. However, ongoing research and technological advancements are addressing these challenges.