Introduction
Neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system, play a crucial role in our thoughts, feelings, and actions. Understanding their structure and function is essential for students of high school psychology. This comprehensive neuron worksheet has been designed to provide students with a deep dive into the workings of neurons.

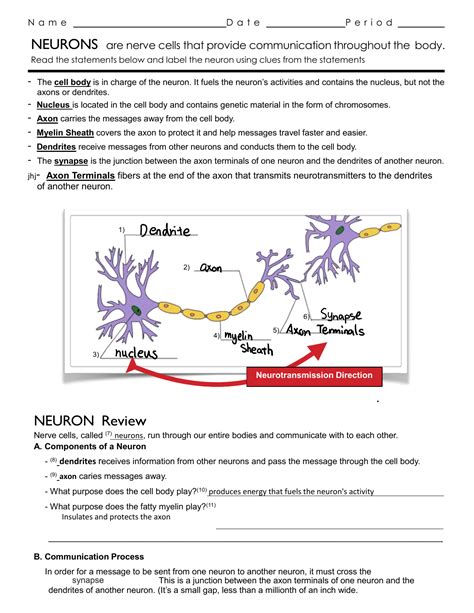
Neuron Structure
Cell Body (Soma)
- Contains the nucleus, which contains the cell’s DNA
- Controls the neuron’s activities and metabolism
Dendrites
- Short, branching extensions of the cell body that receive signals from other neurons
- Increase the neuron’s surface area, allowing for more connections
Axon
- Long, slender extension of the cell body that transmits signals away from the cell body
- Covered in a myelin sheath, which speeds up signal transmission
Axon Terminal
- End of the axon that releases neurotransmitters (chemical messengers)
Neuron Function
Resting Potential
- Neuron is at rest, maintaining a negative charge inside relative to the outside due to the sodium-potassium pump
- Sodium-potassium pump actively transports three sodium ions out of the cell for every two potassium ions that it moves in
Action Potential
- When a neuron receives a signal strong enough to reach the “threshold of excitation,” its membrane depolarizes
- Sodium channels open, allowing sodium ions to rush into the cell, causing the membrane potential to reverse
- Action potential travels down the axon, opening sodium channels in adjacent sections of the membrane
Refractory Period
- Brief period after an action potential when the neuron cannot generate another action potential
- Ensures that signals travel in one direction down the axon
Synaptic Transmission
- Communication between neurons occurs at synapses
- Axon terminal releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
- Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the dendrite of the postsynaptic neuron, causing it to depolarize or hyperpolarize
Types of Neurons
Sensory Neurons
- Transmit sensory information from the body to the central nervous system
Motor Neurons
- Transmit signals from the central nervous system to muscles, glands, and organs
Interneurons
- Connect sensory and motor neurons within the central nervous system
Applications of Neuron Knowledge
Understanding neurons has paved the way for numerous advancements in psychology, medicine, and technology:
- Neurological Disorders: Studying neurons has helped researchers develop treatments for neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and epilepsy.
- Artificial Intelligence: The understanding of neuron function has inspired the development of artificial neural networks, which are widely used in machine learning and other AI applications.
- Bioelectronics: Scientists are exploring the use of neurons as living components in electronic devices, such as neurocomputers and biosensors.
Conclusion
This neuron worksheet provides a thorough understanding of the structure, function, and applications of neurons. By delving into the intricate workings of these vital cells, high school psychology students can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the human brain and the role it plays in our daily lives.