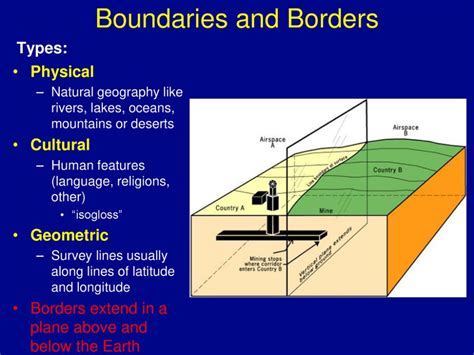
Understanding Natural Borders
Boundaries play a crucial role in shaping the political, economic, and cultural landscapes of the world. Natural borders, in particular, have exerted a significant influence on human geography throughout history. Natural barriers such as mountain ranges, deserts, and rivers have often acted as physical barriers separating different populations and shaping their interactions.

In Advanced Placement Human Geography (AP Human Geo), the concept of natural borders is a key element of the study of political boundaries. Students delve into the various types of natural borders, their impacts on human movement and settlement, and their role in shaping geopolitical dynamics.
Types of Natural Borders
AP Human Geo classifies natural borders into four main categories:
-
Mountain Ranges: Towering mountains and mountain ranges form formidable obstacles that hinder human movement and communication. They can create natural barriers between different regions, influencing cultural and linguistic diversity.
-
Deserts: Vast and unforgiving deserts, with their extreme temperatures, lack of water, and shifting sands, act as barriers to settlement and trade. They often separate densely populated areas and create challenges for transportation and communication.
-
Rivers: Major rivers can serve as both physical barriers and transportation routes. They can impede movement across their waterways, while also providing a means for trade and communication.
-
Oceans: Vast oceans, with their deep waters and treacherous currents, constitute significant natural borders. They can effectively isolate coastal regions from inland areas and shape the distribution of human populations.
Impacts of Natural Borders
Natural borders have profound impacts on human societies in various ways:
Physical Barriers
Natural borders act as physical barriers that hinder movement and communication. Mountain ranges impede trade and migration, creating natural divides between populations. Deserts, with their harsh conditions, pose challenges for travel and settlement. Rivers can restrict movement across their channels, especially during times of flooding.
Cultural and Linguistic Diversity
Natural borders have contributed to cultural and linguistic diversity by separating different populations. Mountain ranges and deserts have acted as barriers, preventing the free flow of ideas and cultures. As a result, distinct cultures and languages have developed in isolated regions.
Geopolitical Dynamics
Natural borders have influenced geopolitical dynamics by shaping political boundaries and military strategies. Mountain ranges, for instance, have often served as natural defenses, providing protection from invasions. Rivers have been used as natural frontiers, marking the limits of political territories.
Examples of Natural Borders
Numerous examples of natural borders can be found around the world:
-
The Himalayas form a towering barrier between the Indian subcontinent and the Tibetan Plateau, separating distinct cultural and linguistic regions.
-
The Sahara Desert acts as a vast and inhospitable barrier in North Africa, isolating sub-Saharan Africa from the Mediterranean Basin.
-
The Amazon River meanders through South America, creating a natural divide between the densely populated coastal regions and the sparsely populated Amazon rainforest.
-
The Pacific Ocean separates North America from Asia, creating a significant natural border between the two continents.
Conclusion
Natural borders play a crucial role in shaping the human experience. They influence human movement and settlement, contribute to cultural and linguistic diversity, and shape geopolitical dynamics. Understanding the concept of natural borders is essential for students of AP Human Geo as it provides insights into the complex relationship between geography and human societies. By studying these natural barriers, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate forces that have shaped the world we live in.