Multinational States: An Overview
A multinational state is a country that encompasses multiple nationalities and ethnic groups within its borders. It is a politically complex entity characterized by diverse languages, cultures, and histories. Multinational states often face challenges in balancing the needs and aspirations of different ethnic groups, maintaining political stability, and promoting economic growth.

Characteristics of Multinational States
- Multiple Nationalities: Multinational states are home to several distinct national groups, each with its own language, culture, and identity.
- Political Complexity: Governing multinational states requires careful balancing of power and representation among different ethnic groups. This can lead to political instability if one group feels marginalized or discriminated against.
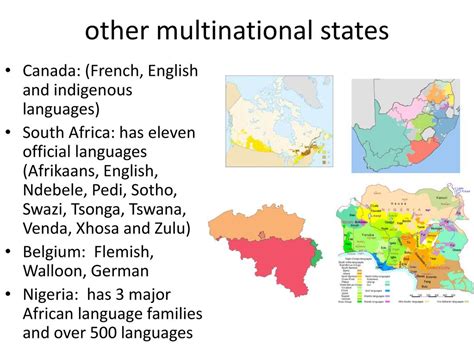
- Linguistic Diversity: Multinational states often have multiple official languages, reflecting the linguistic diversity of their populations. This can present challenges in communication, education, and governance.
- Cultural Heterogeneity: Different ethnic groups within multinational states may have unique customs, traditions, and beliefs. Respecting and preserving cultural diversity is crucial for maintaining social cohesion.
Challenges Faced by Multinational States
- Nationalism and Separatism: Ethnic nationalism and separatist movements can pose a threat to the unity and territorial integrity of multinational states. Dissatisfied groups may demand autonomy or even independence, leading to political tensions and conflict.
- Resource Allocation: Distributing resources fairly among different ethnic groups can be a contentious issue. Balancing economic development with social welfare and cultural preservation is a constant challenge.
- Political Representation: Ensuring that all ethnic groups have adequate representation in government and decision-making bodies is essential for political stability and legitimacy. This can be difficult to achieve in multinational states with power imbalances.
Case Studies of Multinational States
Belgium
Belgium is a classic example of a multinational state, with two major language groups: the Dutch-speaking Flemings and the French-speaking Walloons. After decades of tension and political disputes, Belgium has adopted a power-sharing system to address the challenges of managing a multinational population.
India
India is a diverse and populous multinational state with over 200 languages and 8 major religions. The country has a long history of balancing the interests of different ethnic groups and promoting unity. However, challenges such as regionalism, caste discrimination, and linguistic conflicts continue to test India’s multinational character.
Switzerland
Switzerland is renowned for its successful management of multinationalism. With four official languages (German, French, Italian, and Romansh) and distinct cultural and religious identities, Switzerland has found a balance between maintaining diversity and promoting national cohesion.
Conclusion
Multinational states are complex political entities that present both challenges and opportunities. By understanding the unique characteristics and challenges of multinational states, we can better appreciate the complexities of global governance and the importance of promoting inclusion, diversity, and respect in societies worldwide.