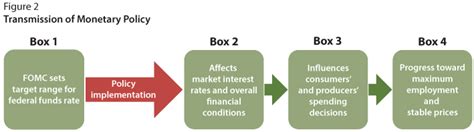
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by the Federal Reserve (Fed) to influence the supply of money and credit in the economy. These actions aim to achieve specific economic goals, such as price stability, full employment, and moderate long-term interest rates.

Tools of Monetary Policy
The Fed has two main tools of monetary policy:
- Open Market Operations: The Fed buys and sells government securities in the open market. When the Fed buys securities, it increases the money supply. When it sells securities, it decreases the money supply.
- Discount Rate: The Fed sets the discount rate, which is the interest rate charged to commercial banks when they borrow from the Fed. By lowering the discount rate, the Fed encourages banks to borrow more money, which increases the money supply. By raising the discount rate, the Fed discourages banks from borrowing, which decreases the money supply.
Goals of Monetary Policy
The Fed’s monetary policy aims to achieve three primary goals:
- Price Stability: The Fed aims to keep inflation under control by targeting a low and stable inflation rate. Inflation is a general rise in the prices of goods and services.
- Full Employment: The Fed aims to promote a high level of employment by encouraging economic growth. Full employment means that nearly everyone who wants a job can find one.
- Moderate Long-Term Interest Rates: The Fed aims to keep long-term interest rates at a moderate level to support economic growth and stability. Low interest rates encourage businesses to invest and consumers to spend, while high interest rates can slow down economic growth.
Effects of Monetary Policy
Monetary policy can have significant effects on the economy:
- Economic Growth: Expansionary monetary policy, such as lowering interest rates or increasing the money supply, can stimulate economic growth by encouraging spending and investment. However, excessive expansionary policy can lead to inflation.
- Inflation: If the money supply increases too rapidly, it can lead to inflation. Inflation erodes the value of money and reduces purchasing power.
- Interest Rates: Monetary policy directly affects interest rates. Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, while higher interest rates discourage borrowing and spending.
- Financial Markets: Monetary policy influences the stock market and other financial markets by affecting interest rates and economic growth prospects.
Evaluating Monetary Policy
The effectiveness of monetary policy depends on several factors, including:
- Economic Conditions: The state of the economy can affect the response to monetary policy. For example, expansionary policy may be less effective during an economic recession than during a period of high growth.
- Time Lags: Monetary policy changes take time to affect the economy. The impact of a policy change may not be felt for several months or even years.
- Expectations: Market participants’ expectations about future economic conditions can influence the effectiveness of monetary policy.
Recent Developments in Monetary Policy
In recent years, the Fed has implemented several unconventional monetary policy measures, including:
- Quantitative Easing: The Fed has purchased large amounts of government and mortgage-backed securities to increase the money supply and support economic growth.
- Negative Interest Rates: Some central banks, such as the European Central Bank, have experimented with negative interest rates, where banks pay to deposit money at the central bank.
- Forward Guidance: The Fed has provided forward guidance about its future monetary policy intentions to reduce uncertainty and influence market expectations.
Future of Monetary Policy
The future of monetary policy remains uncertain. Central banks are facing challenges such as low inflation, rising inequality, and the impact of technological advancements. It is likely that monetary policy will continue to evolve and adapt to meet these challenges.
Tables
Table 1: The Fed’s Monetary Policy Targets
| Target | Description |
|---|---|
| Price Stability | Inflation rate of 2% |
| Full Employment | Unemployment rate of 4.5% |
| Moderate Long-Term Interest Rates | 10-year Treasury rate of 3% |
Table 2: The Effects of Monetary Policy
| Effect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Economic Growth | Stimulates economic growth |
| Inflation | Raises inflation |
| Interest Rates | Lowers interest rates |
| Financial Markets | Influences stock and bond markets |
Table 3: The Fed’s Monetary Policy Tools
| Tool | Effect |
|---|---|
| Open Market Operations | Changes the money supply |
| Discount Rate | Affects bank lending |
Table 4: Unconventional Monetary Policy Measures
| Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Easing | Purchases of securities |
| Negative Interest Rates | Charging banks to hold deposits |
| Forward Guidance | Providing information about future policy intentions |