Mitosis, a fundamental cellular process, lies at the heart of growth, development, and tissue repair. This intricate process ensures the precise duplication of genetic material, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the parent cell’s DNA. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the profound consequences of mitosis, exploring its multifaceted implications for cellular biology and human health.

Understanding Mitosis: A Deep Dive
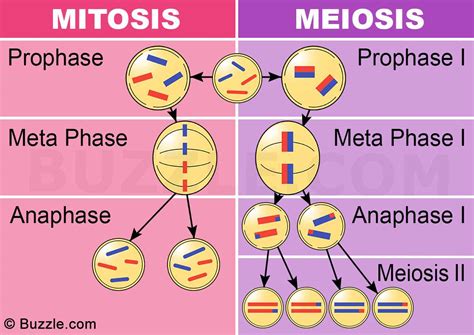
Mitosis can be conceptualized as a finely orchestrated symphony of cellular events, consisting of several distinct phases:
- Prophase: Chromosomes, the thread-like structures containing genetic material, become visible and condense. The nuclear envelope, a membrane surrounding the nucleus, breaks down.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the equator of the cell, forming a metaphase plate.
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids, identical copies of each chromosome, separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase: The separated chromosomes reach the poles, and the nuclear envelope re-forms around each set of chromosomes.
Mitosis Results In: Unveiling the Consequences
The primary outcome of mitosis is the production of two genetically identical daughter cells from a single parent cell. This process has far-reaching implications for a wide array of biological functions:
- Growth and Development: Mitosis fuels the exponential growth of multicellular organisms by generating new cells for the expansion of tissues and organs.
- Tissue Repair: Mitosis enables the replacement of damaged or worn-out cells, facilitating the healing of wounds and the maintenance of tissue integrity.
- Asexual Reproduction: In some organisms, mitosis serves as the sole method of reproduction, resulting in offspring genetically identical to the parent.
Mitosis and Cancer: A Double-Edged Sword
While mitosis is essential for normal physiological processes, it can also contribute to the development of cancer. Uncontrolled mitosis, often caused by genetic mutations, can lead to the formation of abnormal cells that divide excessively and form tumors.
- Cancer Treatment: Understanding mitosis and its regulation are crucial for developing cancer therapies that target and disrupt the uncontrolled cell division.
Mitosis: A Key Player in Human Health
Mitosis plays a pivotal role in maintaining the health and well-being of humans.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Mitosis facilitates the proliferation of stem cells, which have the remarkable ability to differentiate into specialized cell types. This holds promise for regenerative medicine and the treatment of various diseases.
- Gene Therapy: Mitosis assists in the delivery of therapeutic genes into cells, enabling the potential treatment of genetic disorders and diseases such as cancer.
Innovative Applications: Expanding the Horizons of Mitosis
The implications of mitosis extend beyond its fundamental biological roles. By harnessing its power, novel applications are emerging:
- Biomanufacturing: Mitosis can be leveraged to produce large quantities of specific cell types for use in research, drug discovery, and the development of bioengineered tissues.
- Tissue Regeneration: Understanding mitosis can guide the development of biomaterials and scaffolds that promote cell division and facilitate tissue repair.
Tables: Illuminating Mitosis’s Impact
| Phase of Mitosis | Key Events |
|---|---|
| Prophase | Chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope breaks down |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes align at the equator |
| Anaphase | Sister chromatids separate, move to opposite poles |
| Telophase | Chromosomes reach the poles, nuclear envelope re-forms |
| Biological Outcomes of Mitosis |
|—|—|
| Growth and development |
| Tissue repair |
| Asexual reproduction |
| Mitosis and Cancer |
|—|—|
| Uncontrolled mitosis can lead to tumor formation |
| Understanding mitosis aids in cancer treatment development |
| Innovative Applications of Mitosis |
|—|—|
| Biomanufacturing |
| Tissue regeneration |
Conclusion: Mitosis, the Engine of Life
Mitosis stands as a cornerstone of cellular biology, driving growth, development, and tissue repair. Its implications extend far and wide, influencing everything from cancer treatment to regenerative medicine. As our understanding of mitosis deepens, we unlock the potential to harness its power, paving the way for groundbreaking innovations that will shape the future of human health and beyond.