Introduction
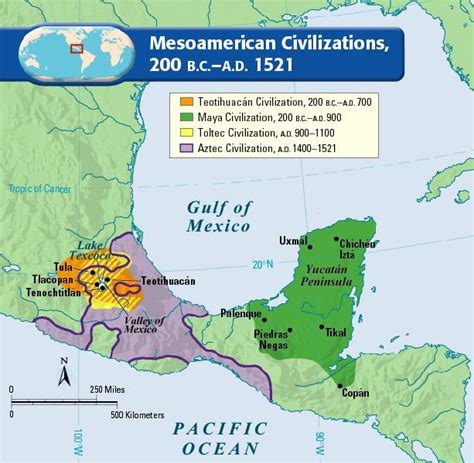
The Mexica, also known as the Aztecs, were an advanced civilization that flourished in the Valley of Mexico from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Their empire extended over a vast territory, encompassing present-day Mexico, Guatemala, and Belize. In AP World History, the Mexica are studied as a prime example of a successful pre-Columbian society.

Rise and Expansion of the Mexica Empire
The Mexica originated from the nomadic Chichimeca people who migrated to the Valley of Mexico around the 13th century. They established their capital at Tenochtitlan, an island city built on Lake Texcoco. Under the leadership of skilled leaders like Moctezuma I and Moctezuma II, the Mexica gradually expanded their territory through military conquest and alliances.
Table 1: Expansion of the Mexica Empire
| Period | Territory |
|---|---|
| 1325-1440 | Central Valley of Mexico |
| 1440-1481 | Guerrero and Oaxaca |
| 1481-1519 | Gulf Coast and Chiapas |
| 1519-1521 | Guatemalan Highlands and Belize |
Society and Culture
The Mexica society was highly organized and stratified. The emperor, known as the Huey Tlatoani, held absolute power. The nobility, priests, and military elite formed the upper class, while the commoners, artisans, and laborers made up the majority of the population.
Table 2: Mexica Social Structure
| Class | Role |
|---|---|
| Huey Tlatoani | Emperor |
| Pipiltin | Nobility and priests |
| Macehualtin | Commoners |
| Tlacotin | Artisans |
| Tlamacazque | Laborers |
The Mexica were polytheistic and believed in a pantheon of gods and goddesses. The most important deities were Huitzilopochtli (the god of war) and Quetzalcoatl (the god of wisdom and creation). Human sacrifice was an integral part of Mexica religious rituals.
Economy and Agriculture
The Mexica economy was based on agriculture, trade, and tribute. They developed advanced farming techniques, such as chinampas (raised fields), to increase crop yields. The Mexica traded their surplus agricultural products, as well as luxury goods like jewelry, textiles, and pottery.
Table 3: Mexica Agriculture and Economy
| Crop | Yield |
|---|---|
| Maize | 600-800 bushels per acre |
| Beans | 400-600 bushels per acre |
| Squash | 200-300 bushels per acre |
| Tomatoes | 100-150 bushels per acre |
Collapse of the Mexica Empire
The Mexica Empire reached its peak in the early 16th century under the rule of Moctezuma II. However, their empire collapsed rapidly after the arrival of Spanish conquistadors led by Hernán Cortés in 1519. Cortés exploited divisions within the empire and forged alliances with indigenous groups who resented Mexica rule.
In 1521, after a two-year siege, the Mexica capital of Tenochtitlan fell to the Spanish. The Mexica Empire was destroyed, and the Spanish established their rule over the region.
Legacy of the Mexica
Despite their relatively short existence, the Mexica left a lasting legacy on the history of Mexico and Central America. Their advanced civilization, sophisticated agricultural techniques, and unique cultural practices continue to influence the region today.
Table 4: Legacy of the Mexica
| Legacy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Chinampas and other farming techniques are still used in Mexico. |
| Architecture | Mexica pyramids, palaces, and temples are architectural marvels. |
| Art | Mexica sculptures, paintings, and codices provide valuable insights into their culture and history. |
| Calendar | The Mexica calendar is a complex and accurate timekeeping system. |
| Language | Many Nahuatl words have been incorporated into Spanish and other Mesoamerican languages. |
Tips and Tricks for AP World History Students
- Study the Mexica Empire as a case study of a successful pre-Columbian society.
- Analyze the factors that contributed to their rise and expansion.
- Understand the complexities of Mexica social structure, religion, and economy.
- Be aware of the factors that led to the collapse of the Mexica Empire.
- Use specific examples from Mexica history to illustrate key concepts in AP World History.