Definition

Mercantilism is an economic theory that flourished in Europe during the 16th and 17th centuries. It held that a nation’s wealth and power were directly linked to its ability to accumulate gold and silver.
Key Features
- Expansion of Colonial Empires: Mercantilist nations sought to establish colonies to secure sources of raw materials and markets for their manufactured goods.
- Protectionism: High tariffs and other barriers were imposed to protect domestic industries from foreign competition.
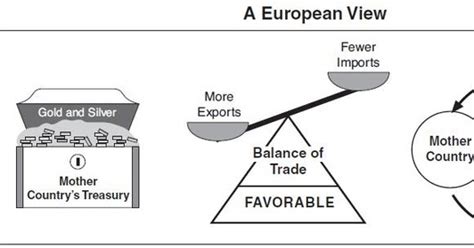
- Bullionism: Gold and silver were seen as the ultimate measures of wealth. Governments sought to increase their reserves through trade surpluses and exploitation of colonies.
- State Intervention: Governments played an active role in regulating trade, industry, and finance to maximize economic output.
Impact on Global Economy
Mercantilism had a profound impact on global economic development:
- Increased Trade: European nations competed fiercely for colonial possessions, leading to a surge in global trade.
- European Dominance: Mercantilist policies contributed to the rise of European economic and political dominance over other parts of the world.
- Exploitation of Colonies: Indigenous populations in colonies were often exploited to provide cheap labor and resources for metropolitan economies.
- War and Conflict: Competition for resources and colonies often led to military conflicts between European powers.
Decline of Mercantilism
By the 18th century, mercantilism began to decline due to factors such as:
- Technological Advancements: New innovations reduced transportation costs and made it easier for goods to be produced and traded internationally.
- Enlightenment Ideas: Philosophers argued against the restrictive policies of mercantilism and promoted free market principles.
- Industrial Revolution: The rise of industrialization shifted the focus from accumulating bullion to technological advancement and productivity.
Mercantilism in AP World History Curriculum
The College Board’s Advanced Placement (AP) World History curriculum includes mercantilism as a key concept in the following units:
- Unit 1: The Global Tapestry (1450-1750)
- Unit 4: Power, Revolution, and Reform (1750-1914)
Tables
Table 1: Key Measures of Mercantilism
| Feature | Definition |
|---|---|
| Colonialism | Establishing overseas territories to control resources and markets |
| Protectionism | Imposing tariffs and other barriers to protect domestic industries |
| Bullionism | Aiming to accumulate gold and silver as measures of wealth |
| State Intervention | Government regulation of trade, industry, and finance |
Table 2: Impact of Mercantilism on Global Economy
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Trade | Spurred global trade due to competition for colonies |
| European Dominance | Led to the rise of European economic and political power |
| Exploitation of Colonies | Indigenous populations exploited for cheap labor and resources |
| War and Conflict | Competition for resources and colonies led to military conflicts |
Table 3: Reasons for the Decline of Mercantilism
| Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | Reduced transportation costs and facilitated international trade |
| Enlightenment Ideas | Promoted free market principles and challenged mercantilist restrictions |
| Industrial Revolution | Shifted focus from bullion accumulation to productivity and innovation |
Table 4: Common Mistakes to Avoid When Studying Mercantilism
| Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
| Misunderstanding the goal | Confusing the goal of mercantilism with the simple accumulation of wealth |
| Oversimplifying government role | Ignoring the complex and varying roles of governments in implementing mercantilist policies |
| Ignoring negative consequences | Overemphasizing the benefits of mercantilism and neglecting its negative impacts on colonies and non-European economies |
| Failing to consider historical context | Not recognizing the specific political, economic, and social circumstances that shaped the development and implementation of mercantilism |
Strategies for Understanding Mercantilism
- Analyze primary sources such as economic treatises and government documents to gain a firsthand perspective on mercantilist theories.
- Trace the development of mercantilism through different European countries, identifying similarities and differences in their policies.
- Compare mercantilism with other economic theories, such as capitalism and free market economics, to identify the key distinguishing features.
- Evaluate the long-term impact of mercantilism on both European and non-European societies.
Conclusion
Mercantilism was a significant economic theory that shaped global events during the early modern period. Its principles of colonialism, protectionism, bullionism, and state intervention played a crucial role in shaping the distribution of wealth and power around the world. Understanding mercantilism is essential for comprehending the development of modern capitalism and the origins of global economic inequality.