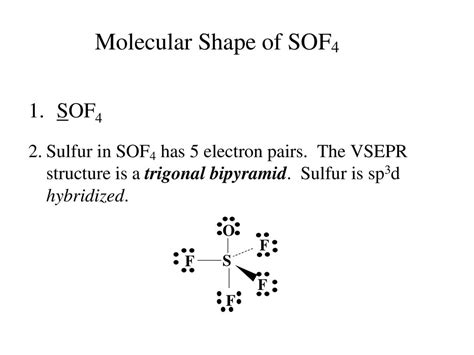
The Lewis structure of SOF₄ depicts the arrangement of atoms and bonds within the sulfur tetrafluoride molecule. Understanding this structure is crucial in unraveling the molecule’s properties and behavior.

Molecular Geometry of SOF₄
The Lewis structure of SOF₄ reveals a tetrahedral molecular geometry. The sulfur (S) atom is at the center, bonded to four fluorine (F) atoms. The four S-F bonds are arranged in a tetrahedral shape, with each F atom occupying one corner of the tetrahedron.
Bonding in SOF₄
The sulfur atom in SOF₄ has six valence electrons, while each fluorine atom has seven valence electrons. To achieve a stable configuration, each fluorine atom shares one of its valence electrons with the sulfur atom, forming four covalent bonds. The remaining two valence electrons on the sulfur atom form a lone pair.
The Lewis structure of SOF₄ can be represented as:
F | F---S---F | F
where the solid lines represent the covalent bonds and the two dots on the sulfur atom represent the lone pair.
Polarity of SOF₄
The arrangement of the lone pair on the sulfur atom creates an uneven distribution of electrons within the molecule, resulting in a polar covalent bond. The fluorine atoms have a partial negative charge due to the electronegativity difference between fluorine and sulfur, while the sulfur atom has a partial positive charge.
Properties of SOF₄
- Colorless gas at room temperature
- Highly reactive and corrosive
- Toxic and can cause severe burns and respiratory problems
- Used as a fluorinating agent in chemical synthesis
Applications of SOF₄
The unique properties of SOF₄ make it a useful reagent in various applications, including:
- Semiconductor industry: Etching of silicon wafers to create electronic circuits
- Chemical warfare: As a component in chemical warfare agents such as VX and sarin
- Organic synthesis: Fluorination of various organic compounds
- Medical applications: As an antiseptic and disinfectant
Pain Points and Motivations
The use of SOF₄ comes with certain pain points and motivations that drive its development and applications:
Pain Points:
- High toxicity and corrosiveness
- Difficulty in handling and storage
- Environmental concerns due to its persistence and ozone-depleting potential
Motivations:
- Need for a highly effective fluorinating agent
- Development of safer and more environmentally friendly alternatives
- Exploration of new applications in medicine and technology
Innovations and Future Applications
Research is ongoing to address the pain points associated with SOF₄ and to explore its potential in novel applications. Some recent innovations and future applications include:
- Development of non-toxic SOF₄ derivatives: Scientists are investigating halogenated derivatives of SOF₄ that offer similar reactivity but reduced toxicity.
- Production of nanomaterials: SOF₄ is used in the synthesis of fluorinated graphene and other nanomaterials with unique properties.
- Medical advancements: SOF₄-based compounds are being explored as potential cancer therapeutics and antimicrobial agents.
Tables
Table 1: Physical Properties of SOF₄
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 102.07 g/mol |
| Boiling point | -43.8 °C |
| Melting point | -122.5 °C |
| Density | 1.79 g/cm³ |
Table 2: Chemical Properties of SOF₄
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Reactivity | Highly reactive |
| Flammability | Not flammable |
| Corrosiveness | Highly corrosive |
| Toxicity | Toxic |
Table 3: Applications of SOF₄
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Semiconductor industry | Etching of silicon wafers |
| Chemical warfare | Component in VX and sarin |
| Organic synthesis | Fluorination of organic compounds |
| Medical applications | Antiseptic and disinfectant |
Table 4: Pain Points and Motivations
| Pain Point | Motivation |
|---|---|
| Toxicity and corrosiveness | Development of safer alternatives |
| Environmental concerns | Exploration of environmentally friendly options |
| Need for fluorinating agent | Research into new applications |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the molecular geometry of SOF₄?
Answer: Tetrahedral
2. Why is SOF₄ polar?
Answer: Due to the presence of a lone pair on the sulfur atom.
3. What are the hazards associated with SOF₄?
Answer: Toxicity, corrosiveness, and potential ozone depletion.
4. What are some applications of SOF₄?
Answer: Semiconductor industry, chemical warfare, organic synthesis, and medical applications.
5. What are the pain points associated with SOF₄?
Answer: Toxicity, corrosiveness, environmental concerns.
6. What are the motivations for research on SOF₄?
Answer: Development of safer alternatives, exploration of new applications, addressing environmental concerns.