Understanding the Framework
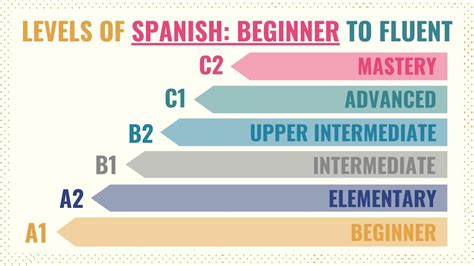
The Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) establishes a standardized scale to measure language proficiency, including Spanish. This framework divides language skills into six levels:

- A1: Beginner
- A2: Elementary
- B1: Intermediate
- B2: Upper Intermediate
- C1: Advanced
- C2: Proficient
Each level corresponds to specific linguistic abilities and knowledge. Let’s delve into the details:
A1: Beginner
At this level, learners possess a basic understanding of Spanish grammar and vocabulary. They can understand simple phrases and questions related to familiar topics, introduce themselves, and engage in basic conversations about personal information.
A2: Elementary
Learners expand their vocabulary and grammatical knowledge, enabling them to communicate more effectively. They can understand short conversational texts, ask and answer questions, and describe their daily routine and immediate surroundings.
B1: Intermediate
This level marks a significant milestone in language proficiency. Learners can understand the main ideas of complex texts, discuss abstract topics, and express their thoughts and opinions with some degree of fluency. They can also write short, structured texts on familiar subjects.
B2: Upper Intermediate
Learners develop a deeper understanding of Spanish culture and language. They can comprehend extended written and spoken texts, express sophisticated ideas accurately, and participate in discussions on a wide range of topics.
C1: Advanced
Learners achieve a high level of fluency and accuracy in Spanish. They can understand complex texts, both spoken and written, and produce elaborate and well-structured speech. They have a deep understanding of Spanish grammar and can handle idiomatic expressions and colloquialisms.
C2: Proficient
This is the highest level of language proficiency, where learners are virtually indistinguishable from native speakers. They can understand and produce highly complex language in both formal and informal settings, demonstrating exceptional fluency and precision.
Tips and Tricks for Language Mastery
1. Immerse Yourself: Submerge yourself in the language through movies, music, books, and interactions with native speakers.
2. Practice Regularly: Dedicate time to studying grammar, expanding vocabulary, and honing your speaking and writing skills.
3. Find a Language Partner: Collaborate with a native Spanish speaker for regular conversations and feedback.
4. Set Realistic Goals: Avoid overwhelming yourself with overly ambitious targets. Focus on achievable milestones and celebrate your progress.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Fear of Making Mistakes: Embrace errors as learning opportunities.Mistakes help you identify areas for improvement.
2. Translation-Based Learning: Avoid relying solely on direct translation. Immerse yourself in the target language to develop a natural understanding.
3. Neglecting Grammar: While fluency is important, a solid foundation in grammar is essential for effective communication.
4. Overloading with Vocabulary: Focus on building a core vocabulary that you can use confidently. New words will naturally accumulate through immersion.
Conclusion
Mastering Spanish is a rewarding journey that requires dedication, consistency, and a passion for language learning. By understanding the CEFR levels, you can set clear goals, track your progress, and achieve the level of proficiency that aligns with your aspirations.