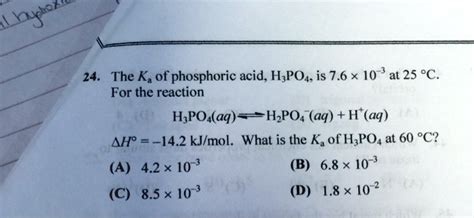Introduction
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4), commonly known as orthophosphoric acid, is a crucial inorganic component that plays a multifaceted role in various scientific and industrial applications. This article delves into the fascinating world of H3PO4, exploring its properties, applications, and potential in groundbreaking fields.

Properties of H3PO4
- Chemical Formula: H3PO4
- Appearance: Colorless, syrupy liquid
- Molecular Weight: 97.99 g/mol
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water
- Density: 1.83 g/cm³
- pKa Values: pKa1 = 2.12, pKa2 = 7.20, pKa3 = 12.35
- Acidity: Triprotic acid (can lose three protons)
- Corrosivity: Highly corrosive to skin and metal
Applications of H3PO4
Fertilizers
H3PO4 is the backbone of fertilizer production, accounting for over 80% of global consumption. Its phosphorus content promotes plant growth and root development, making it essential for agriculture.
Food and Beverages
As an acidulant and sequestrant, H3PO4 enhances flavor, prevents discoloration, and acts as a preservative in a wide range of foods and beverages, including soft drinks, dairy products, and baked goods.
Chemical Processing
H3PO4 is used as a catalyst in the production of chemicals such as fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and detergents. It also plays a role in metal treatment, water purification, and petroleum refining.
Metalworking
H3PO4 is employed in metalworking industries for pickling, polishing, and surface treatment. Its corrosive nature enables the removal of oxides and impurities from metal surfaces.
Potential Applications in Cutting-Edge Fields
The unique properties of H3PO4 hold promise for groundbreaking applications in emerging fields:
- Energy Storage: H3PO4-based flow batteries offer high energy density and long-term stability for grid-scale energy storage.
- Biomedicine: H3PO4 derivatives are used in gene therapy, drug delivery, and tissue engineering due to their biocompatibility and tunable properties.
- Nanotechnology: H3PO4 can be utilized to synthesize nanomaterials with tailored properties for use in electronics, optics, and medical devices.
Ka of H3PO4
The Ka value, or acid dissociation constant, is a measure of the strength of an acid. For H3PO4, the three Ka values are:
| Stage | Ka Value |
|---|---|
| H3PO4 + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + H2PO4- | 7.52 x 10^-3 |
| H2PO4- + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + HPO42- | 6.31 x 10^-8 |
| HPO42- + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + PO43- | 3.63 x 10^-13 |
These values indicate that H3PO4 is a weak acid, with its acidity decreasing with each proton lost.
Tables of Useful Information
Table 1: Physical Properties of H3PO4
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 158 °C |
| Melting Point | 42.35 °C |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.03 kPa (20 °C) |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 1.38 kJ/(kg·K) |
Table 2: Applications of H3PO4
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Fertilizers |
| Food and Beverage | Acidulant, sequestrant, preservative |
| Chemical Processing | Catalyst, water purification |
| Metalworking | Pickling, polishing, surface treatment |
| Biomedical | Gene therapy, drug delivery |
Table 3: Ka Values of H3PO4
| Stage | Ka Value |
|---|---|
| H3PO4 ⇌ H3O+ + H2PO4- | 7.52 x 10^-3 |
| H2PO4- ⇌ H3O+ + HPO42- | 6.31 x 10^-8 |
| HPO42- ⇌ H3O+ + PO43- | 3.63 x 10^-13 |
Table 4: Potential Applications of H3PO4 in Emerging Fields
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Energy Storage | Flow batteries |
| Biomedicine | Gene therapy, drug delivery |
| Nanotechnology | Nanomaterial synthesis |
Conclusion
H3PO4 is a versatile and valuable inorganic compound with a wide range of applications in industry, agriculture, and emerging fields. Its unique properties, such as high acidity and solubility, make it a key ingredient in fertilizers, food additives, and catalysts. With ongoing research, the potential applications of H3PO4 are boundless, paving the way for innovative advancements in science and technology.